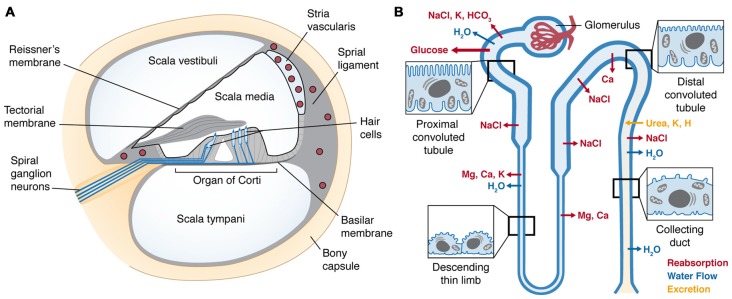
Figure 2.
(A) Cross-section of the cochlear duct, illustrating the perilymph-filled scala vestibuli and scala tympani, separated from the scala media by tight junctions between adjacent cells (black line) of Reissner’s membrane and reticular lamina of the organ of Corti resting on the basilar membrane. Within the organ of Corti are four longitudinal rows of sensory hair cells (in sky blue), under the tectorial membrane. The hair cells are innervated by afferent and efferent fibers (blue lines). Within the lateral wall of the cochlea is the highly-vascularized stria vascularis (upper right); enclosing several capillary beds (red circles) lined by tight-junction-coupled endothelial cells (black lines enclosing red circles) that form the cochlear BLB. (B) A nephron (kidney tubule) showing the glomerulus encapsulating a single capillary bed that gathers the ultrafiltrate from blood. The proximal tubule has a brush border of microvilli that recovers the majority of essential nutrients and ions, and the distal tubule recaptures the remaining nutrients, and excretes specific ions. Sites of major ion movements are shown. Both schematic diagrams are not to relative scale.