Figure 1.
ApoER2 and EphrinB2 Are Required for Activity-Induced New AMPA Receptor Insertion
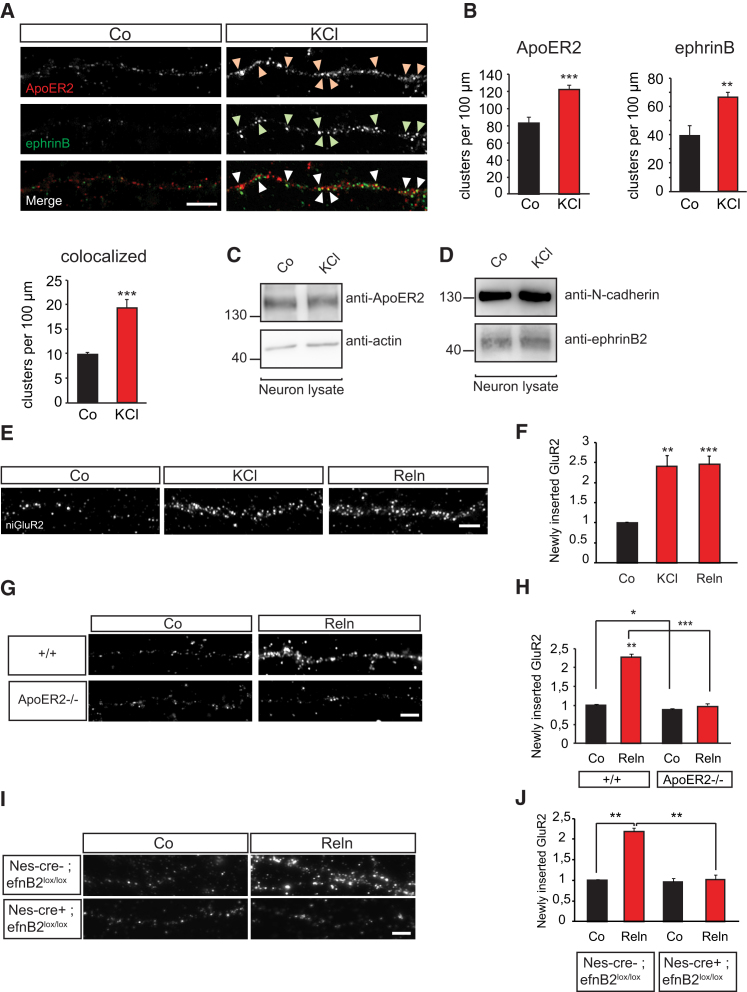
(A and B) Potassium chloride (KCl) stimulation co-clusters ephrinBs with ApoER2. Primary hippocampal neurons were isolated from wild-type mice at E17.5 and stimulated with 10 mM KCl for 10 min at 14 DIV to activate neuronal activity. Microscopic images show fluorescent staining of ApoER2 and ephrinB in dendrites. Arrowheads indicate co-clustering of ApoER2 (red) and ephrinB (green) upon KCl stimulation (A). Quantification of ApoER2, ephrinB, and ApoER2-ephrinB colocalized clusters is shown for n = 5 neurons (B).
(C and D) Neuronal membrane depolarization by KCl does not alter the expression levels of ApoER2 and ephrinB2. Hippocampal neuron cultures were treated with 10 mM KCl for 10 min at 14 DIV to induce neuronal activity and subjected to subsequent western blot analysis. Western blots showing ApoER2 expression levels and control actin levels (C) and ephrinB2 and control N-cadherin expression levels (D).
(E and F) Induction of neuronal activity and activation of ApoER2 induces AMPA receptor insertion in dendritic membranes. Wild-type hippocampal neurons (E17.5) were subjected to AMPA receptor membrane insertion assays. During the assay, neurons were stimulated with 10 mM KCl or concentrated Reelin (Reln) supernatants. Stimulations were conducted for 10 min (KCl) or 3 hr (Reln). Fluorescent images of GluR2 inserted into the dendritic membrane in response to KCl or Reelin (E). Relative fluorescence intensities of newly inserted GluR2 in dendrites of neurons (n = 6) (F).
(G and H) ApoER2 is essential for Reelin-induced membrane insertion of AMPA receptors. AMPA receptor membrane insertion was analyzed in wild-type and ApoER2 knockout hippocampal neurons upon stimulation with Reelin for 3 hr. Fluorescent images represent newly inserted GluR2 in dendritic branches of wild-type (+/+) and ApoER2 knockout (ApoER2−/−) neurons upon Reelin stimulation (G). Quantification shows relative intensities of GluR2 insertion in wild-type and ApoER2 knockout neurons (n = 3) (H).
(I and J) EphrinB2 mediates the membrane insertion of AMPA receptors upon Reelin stimulation. Control and ephrinB2 knockout neurons were subjected to AMPA receptor membrane insertion assays. Images of dendrites showing newly inserted GluR2 in response to Reelin stimulation in control (Nes-cre−; efnB2lox/lox) and ephrinB2 knockout (Nes-cre+; efnB2lox/lox) hippocampal neurons (I). Quantification of relative GluR2 intensities in neuronal dendrites (n = 3) (J).
Scale bars represent 5 μm (A, E, G, and I). Bar graphs show mean ± SEM (shown as error bars). ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001. See also Figure S1.