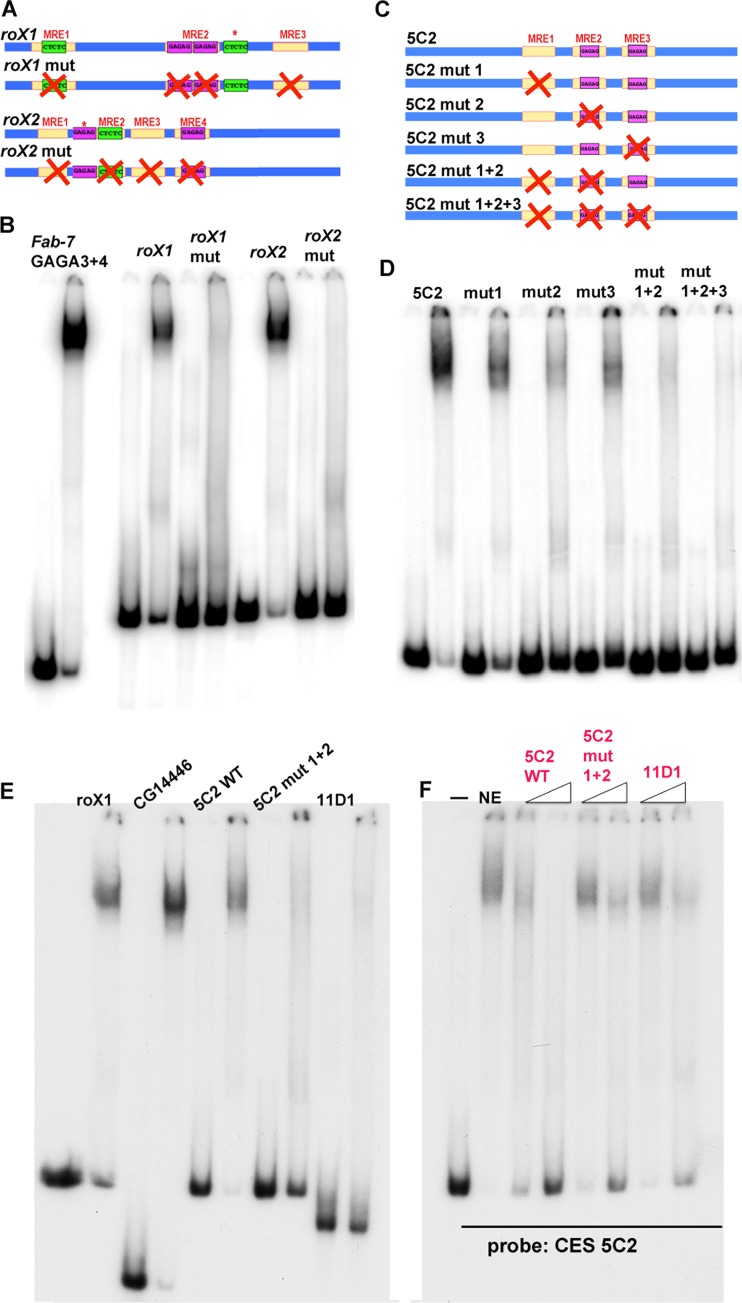
FIG 5.
LBC binding is MRE dependent. (A) Schematic drawing of the wild-type (WT) (top) and mutated (bottom) versions of the 200-bp roX1/roX2 sequences used for EMSAs. Asterisks denote a GA-rich sequence that does not match the position weight matrix for the MRE. (B) Mutations in the roX1 and roX2 MREs abrogate LBC binding. (C) Schematic of the wild-type and mutant versions of the 5C2 probes. (D) Single and combination mutations in three 5C2 MREs differentially affect LBC binding. (E) Comparison of LBC binding to CES 11D1 with other LBC substrates as indicated. (F) Excess unlabeled wild-type 5C2, 5C2 mut1+2, and CES 11D1 DNAs were used to compete for LBC binding to labeled CES 5C2. Fold excess of cold competitor added (left to right): CES 5C2, 12.5× and 100×; CES 5C2 mut1+2, 25× and 200×; CES 11D1, 25× and 200×.