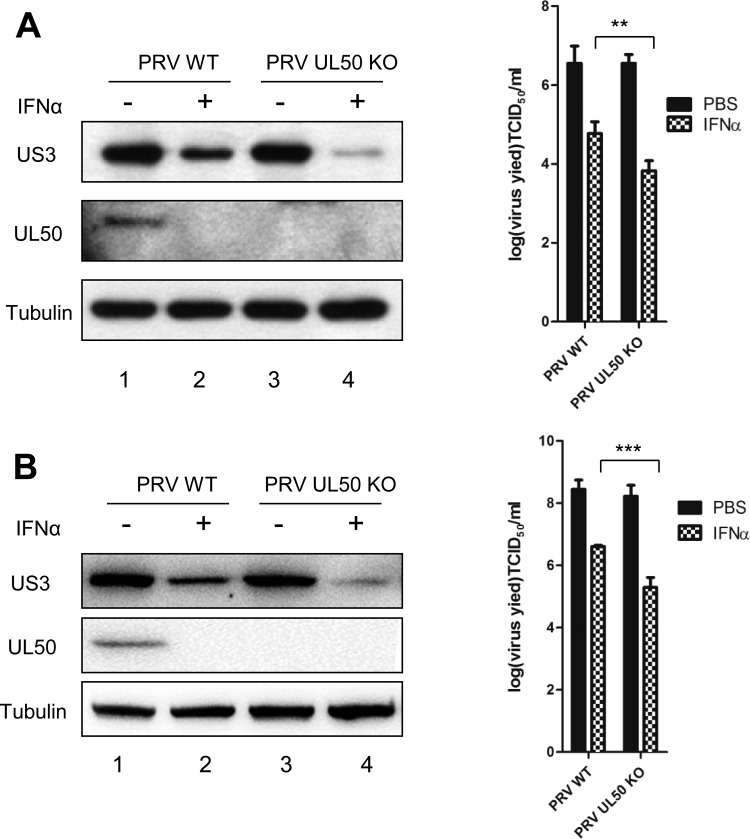
FIG 9.
PRV deficient in UL50 is more sensitive to IFN-α-mediated viral inhibition. (A) PK15 cells were treated with porcine IFN-α (1,000 U/ml). Twenty-four hours later, the cells were infected with either wild-type PRV or recombinant PRV-UL50 KO for 1 h (MOI = 0.1). The infected cells were then incubated in medium containing porcine IFN-α (1,000 U/ml) for an additional 24 h. The cells were harvested and lysed for Western blotting (left) and TCID50 assay (right). (B) CRL cells were treated with porcine IFN-α (500 U/ml). Twelve hours later, the cells were infected with either PRV-WT or recombinant PRV-UL50 KO for 1 h (MOI = 1). The infected cells were then incubated in medium containing porcine IFN-α (500 U/ml) for an additional 24 h. Cells were harvested and lysed for Western blotting (left) and TCID50 assay (right). The virus protein (US3 and UL50) levels were examined by Western blotting, and tubulin was included as a loading control. The results were obtained from three independent experiments and are means and SD. Statistical analyses were performed by ANOVA, using GraphPad Prism software. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.