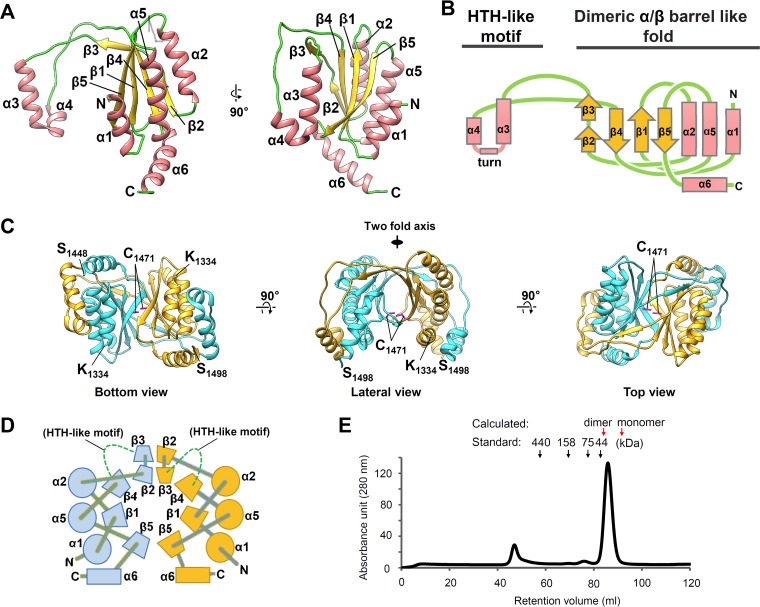
FIG 1.
Crystal structures of HHV-6A IE2-CTD and the dimeric form. (A) The HHV-6A IE2-CTD monomer is shown in a ribbon representation with secondary structural elements assigned. The positions of N- and C-terminal residues are indicated. Only one monomer from the dimeric form is shown for clarity. (B) Topology diagram showing the secondary structure arrangement. α1β1α2β2β3β4α5β5 constitutes a two-layered α/β sandwich fold, while α3 and α4 are distant from the main globular domain and connected by a turn, resulting in a helix-turn-helix (HTH)-like motif. α-Helices and β-strands are represented by pink rectangles and yellow arrows, respectively. The turn is represented by a pink line. (C) Dimeric form of HHV-6A IE2-CTD shown as ribbon models from three different views. The two IE2-CTD molecules are shown in cyan and orange. The N- and C-terminal residues (K1334 and S1498) and the cysteine residues (C1471) (magenta) at the 2-fold axis are indicated. (D) Topology diagram of the two-layered α/β sandwich fold forming a closed barrel with an antiparallel β-sheet arrangement. Circles and trapeziums represent α-helices and β-strands, respectively. Long extrusions, including the HTH-like motif between β3 and β4, are omitted for clarity and represented by green dotted lines. Perpendicularly arranged α6-helices are shown as rectangles. (E) Size exclusion chromatography of purified IE2-CTD. The retention volumes of standards are indicated by arrows and molecular mass labels, and the expected retention volumes for the IE2-CTD dimer (40.8 kDa) and monomer (20.4 kDa) were calculated from the standard curve and are indicated by red arrows. IE2-CTD eluted as a single peak distinct from the void volume (∼45 ml), with a retention volume close to that expected for a dimer.