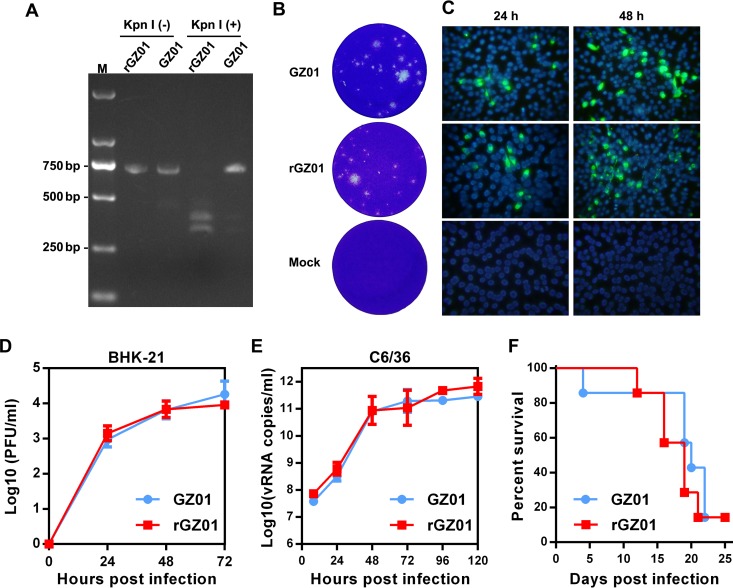
FIG 2.
Comparison of biological characteristics between recovered GZ01 and the parental strain. (A) Identification of the KpnI-marker in recovered ZIKV. Viral RNA was isolated from supernatants of GZ01 and rGZ01 and ZIKV cDNA fragments were amplified by RT-PCR and digested by the endonuclease KpnI. The KpnI-digested PCR products [KpnI (+)] and undigested controls [KpnI (−)] were analyzed by electrophoresis in a 1.5% agarose–TAE gel. Lane M, DNA marker DL 2,000. (B) Plaque morphologies of rGZ01 and parental GZ01. Mock, uninfected BHK-21 cells. (C) BHK-21 cells were infected with an MOI of 0.1 of rGZ01 and GZ01, respectively, and viral E protein expression was monitored by IFA at different time points after infection. Uninfected BHK-21 cells were subjected to IFA and the results were shown in parallel (mock). (D and E) Comparison of the growth kinetics of rGZ01 and GZ01. (D) Infectious viruses in the supernatants of MOI 0.1-infected BHK-21 cells were determined by plaque assay. (E) C6/36 cells were infected with rGZ01 and GZ01 at an MOI of 0.1, culture supernatants were collected at different time points postinfection, and vRNA levels were determined by qRT-PCR. (F) Neurovirulence of rGZ01 and GZ01 in neonatal BALB/c mice. One-day-old BALB/c suckling mice (n = 7) were incubated with 10 PFU of rGZ01 or GZ01, respectively, and the survival statistics were monitored daily.