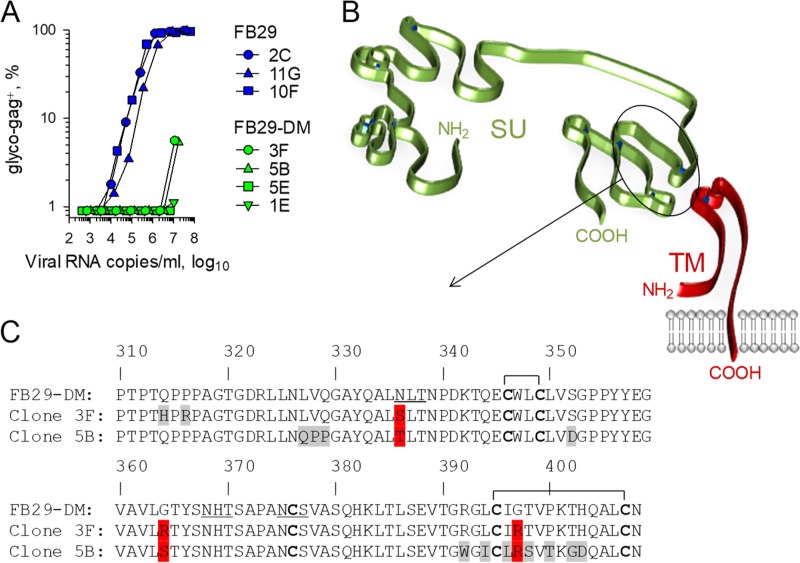
FIG 5.
Infectivity of wild-type and ISD mutant F-MLV clones isolated in JAWSII cell sublines. (A) Frequency of F-MLV-infected (glyco-Gag-positive) M. dunni cells 3 days after infection with the indicated doses of FB29 or FB29-DM viruses produced by the respective JAWSII cell sublines. The results of one representative of two experiments conducted are shown. (B) Schematic representation of the SU and TM domains, based on models proposed for the MLV SU (15) and the MLV TM (21), respectively. The circled region of the SU domain indicates the location where the mutations in clones 3F and 5B of the FB29-DM virus were identified. (C) Section of the amino acid sequence of the envelopes of the index isolate and clones 3F and 5B of the FB29-DM virus. Amino acid positions in gray and red represent unique and common substitutions, respectively. Horizontal brackets indicate the cysteine residues involved in disulfide bonds. Underlined residues denote the N-linked glycosylation sites.