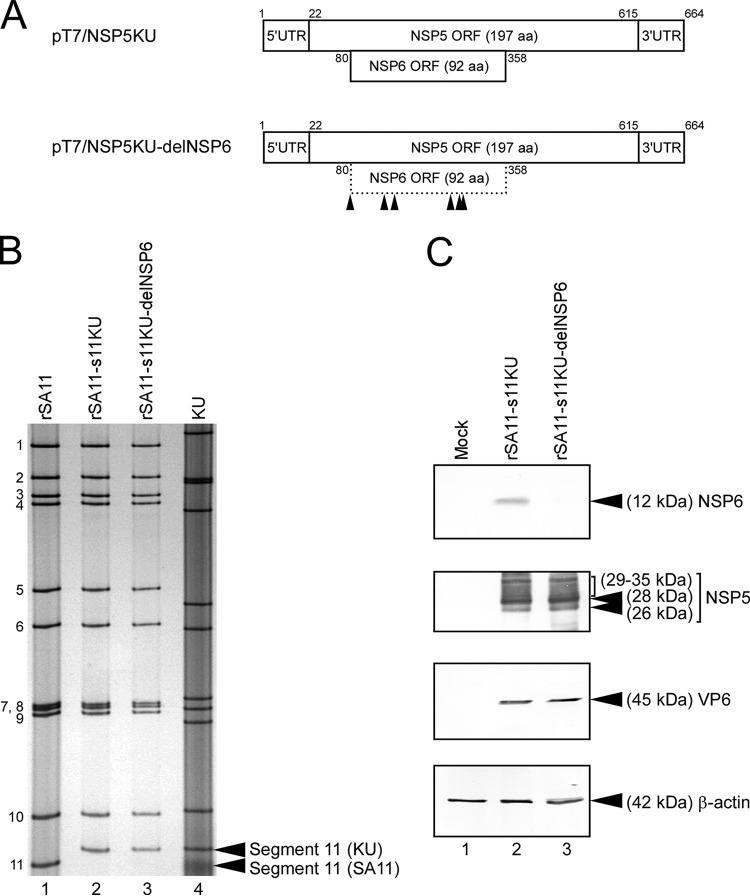
FIG 3.
Generation of recombinant SA11-based monoreassortant viruses having a KU-derived segment 11 capable or incapable of NSP6 expression. (A) Schematic presentation of the plasmids encoding KU segment 11 (NSP5/6 genes) for rescue of the wild-type rSA11-s11KU and mutant rSA11-s11KU-delNSP6 viruses (pT7/NSP5KU and pT7/NSP5KU-delNSP6, respectively). To generate plasmid pT7/NSP5KU-delNSP6, the start codon and five AUG codons in the NSP6 ORF of KU were disrupted by replacing them with ACG codons. The arrowheads indicate the ACG mutation sites. (B) PAGE of viral dsRNAs extracted from rSA11, rSA11-s11KU, rSA11-s11KU-delNSP6, and native KU. Lane 1, dsRNAs from rSA11; lanes 2 and 3, rSA11-s11KU (lane 2) and rSA11-s11KU-delNSP6 (lane 3); lane 4, native KU. The numbers on the left indicate the order of the genomic dsRNA segments of rSA11. (C) Expression of the NSP6 protein and other RVA proteins in MA104 cells infected with rSA11-s11KU or rSA11-s11KU-delNSP6. Whole-cell lysates of infected cells were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-NSP6 antiserum, anti-NSP5 antiserum, anti-VP6 antiserum, or anti-β-actin monoclonal antibody. Shown are mock (lane 1), rSA11-s11KU (lane 2), and rSA11-s11KU-delNSP6 (lane 3) infection.