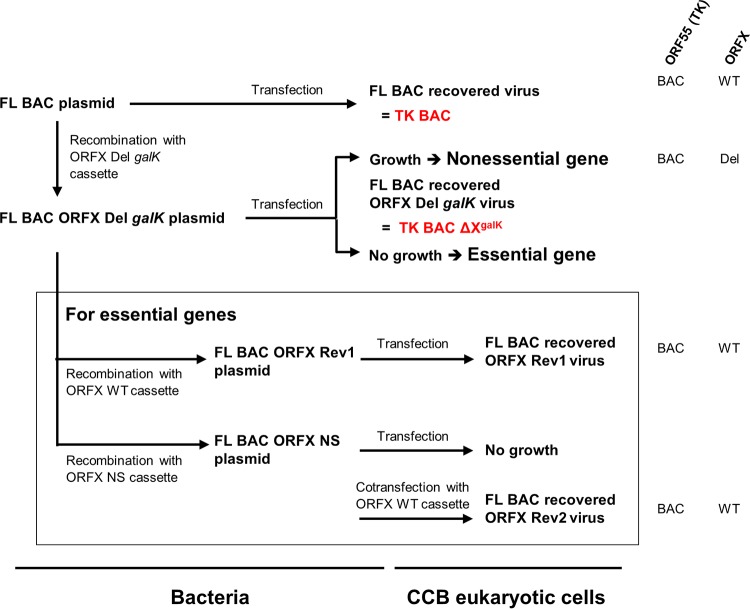
FIG 2.
Production of CyHV-3 recombinants to identify essential and nonessential VTPs. Deleted recombinant plasmids were produced for each ORF predicted to encode a VTP (FL BAC ORFX Del galK plasmids, with “X” standing for the number of the ORFs tested; these included ORF25, ORF32, ORF59, ORF64, ORF65, ORF81, ORF83, ORF99, ORF106, ORF108, ORF115, ORF131, ORF132, ORF136, ORF148, and ORF149). The effect of the deletion on the ability of the BAC plasmid to reconstitute infectious virus was tested by transfection into permissive CCB cells. Subsequently, for each gene identified as essential, two additional recombinant plasmids were produced to revert to wild-type ORFX sequence (FL BAC ORFX Rev1) or to insert a nonsense mutation (FL BAC ORFX NS). Plasmids were transfected into CCB cells to determine their ability to induce reconstitution of infectious virus. As an additional revertant control, FL BAC ORFX NS plasmids were cotransfected into CCB cells together with a fragment encoding the WT sequence of ORFX and flanking regions, in order to facilitate reversion to wild-type ORFX sequence by recombination in eukaryotic cells (FL BAC ORFX Rev2). To simplify the reading of the manuscript, some recombinants were given a short name (in red). The right part of the Fig. summarizes the genotype of the strains for ORF55 (TK) and ORFX. Del, deleted; WT, wild type; BAC, presence of the BAC cassette in the 3′ end of ORF55.