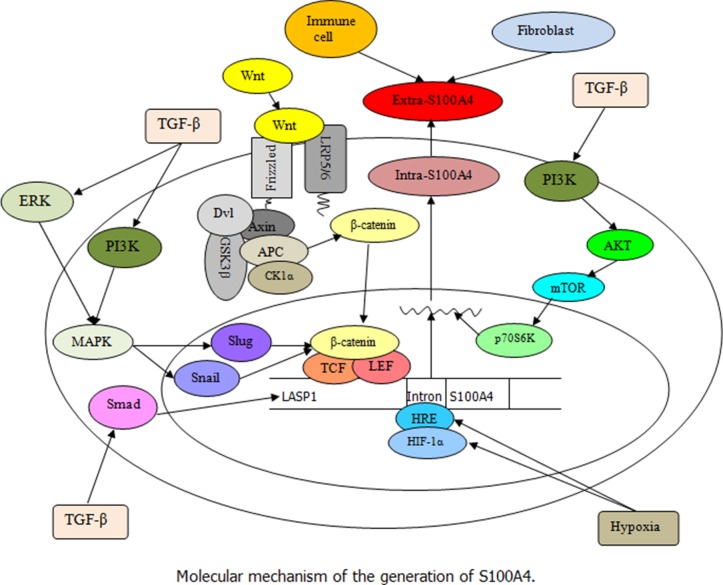
Figure 1. Illustration of S100A4 regulation (Black arrow indicates the promoting effect).
This schema illustrates the regulation and expression of S100A4 in cells. Extra-S100A4 can be produced by fibroblasts, immune cells, and tumor cells. The stimulation of TGF-β results in an increase of LASP1 and S100A4 by activating Smad pathway, and the TGF-β-induced ERK and PI3K signaling leading to slug and snail synergistic regulation of β-catenin/TCF/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor (LEF) is involved in the expression of S100A4. Besides, the interaction of Wnt with the frizzled receptor and the co-receptors low-density lipoprotein receptor-related proteins (LRP) 5/6 could inactivate the β-catenin destruction complex leading to the cytoplasmic accumulation of β-catenin followed by its translocation into the nucleus, where it activates the transcription of target S100A4 gene under the control of a TCF binding motif along with LEF. Moreover, the exposure to hypoxia increases the hypomethylation of the first intron (HRE) of S100A4 gene and enhances the binding of HIF-1α to HRE in tumor cells, thereby promoting the S100A4 transcription levels.