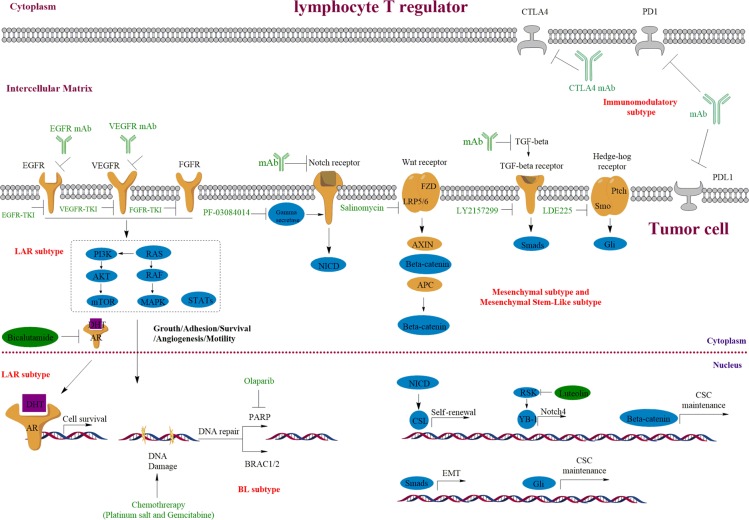
Figure 2. Targeting the growth factor receptors and PARP in TNBC and the important roles of Notch, Wnt/β-catenin, Hedge-hog and TGF-β signaling pathways in TNBC.
Overexpression or mutations of the EGFR, VEGFR, AR and FGFR are common in TNBC, which result in the deregulation of downstream signaling. Receptor specific-monoclonal antibody (mAb) and TKIs are used to block ligand-receptor interaction or kinase activity, which further turnoff their downstream signaling. The BL2 subtype of TNBC could be especially sensitive to these growth signaling inhibition. BRCA1/2 mutations or decreased expression are frequently involved in TNBC initiation and development, which also causes HR deficiency and hypersensitive to PARP inhibition (BL1 subtype). Mesenchymal-like subgroup of TNBC is enriched for genes involved in CSCs regulation and EMT, and corresponding tumors could be sensitive to mAb and inhibitors in these pathways.