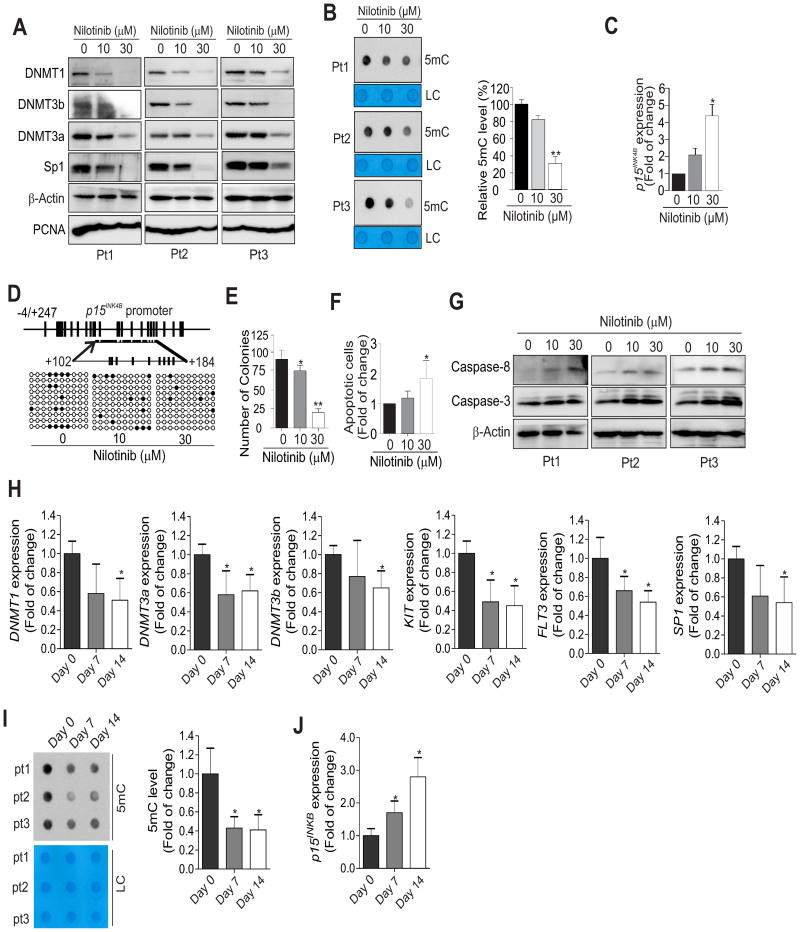
Figure 6.
Nilotinib suppresses DNMT expression, induces DNA hypomethylation and impairs AML patient cell expansion ex vivo and in vivo. A-G, AML patient (Pt) primary cells (n = 3) were treated for 24 h with 0, 10 or 30 μM nilotinib. (A) Cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. (B) The genomic DNA was subjected to dotblot analysis to assess changes in global DNA methylation. (C) qPCR analysis was used to determine p15INK4B gene expression. (D) Bisulfite sequencing was used to examine p15INK4B promoter DNA methylation. Methylated CpG sites are shown as solid circles and open circles indicate non-methylated CpG sites. A representative 10 clones are shown in the dot plot. (E) Colony-forming assays show cell proliferation. (F) Cellular apoptosis was determined by flow cytometry. (G) Western blot analysis was used to detect the activated forms of caspases. H-J, The PBMCs from AML patients (n = 14) receiving nilotinib therapy (day 0, day 7 or day 14) were subjected to qPCR for gene expression (H, J) or dotblot analysis for changes in global DNA methylation (I). In B, C, E, F, H, I and J, data are shown as mean values ± S.D; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.