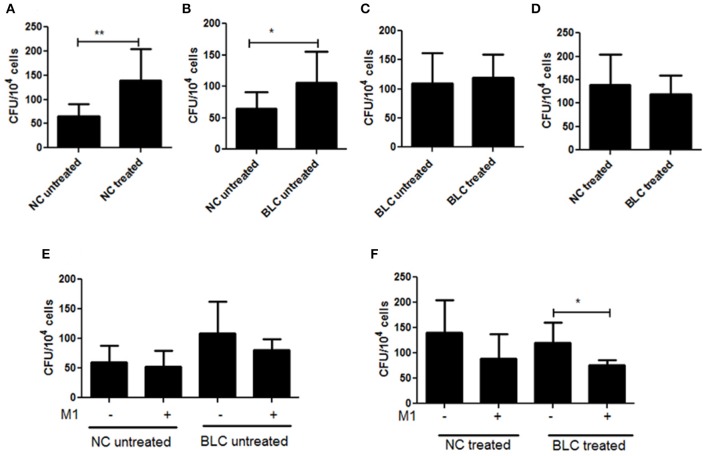
Figure 4.
PBMC derived macrophages from subjects with borderline risk cholesterol profiles showed reduced clearance of intracellular mycobacteria. PBMC derived macrophages were isolated from human volunteers with either normal (NC) or borderline risk (BLC) cholesterol profiles, were either untreated or cholesterol treated and then infected with M.tb H37Rv as discussed in methods. The clearance of mycobacteria by PBMC derived macrophages from the two categories was evaluated by CFU enumeration 48 h post-infection. Bar plots showing CFU enumeration from (A) Cholesterol untreated and treated PBMC derived macrophages of NC; (B) Cholesterol untreated PBMC derived macrophages of NC and BLC; (C) Cholesterol Untreated and treated PBMC derived macrophages of BLC; (D) Cholesterol treated PBMC derived macrophages of NC and BLC; (E) Cholesterol untreated PBMC derived macrophages of NC and BLC with or without M1 treatment and (F) Cholesterol treated PBMC derived macrophages of NC and BLC with or without M1 treatment. Each experiment was carried out at the least three times NC (n = 4) and BLC (n = 3). Statistical analyses were performed as mentioned in methods. Error bars represent ± SD. *P ≤ 0.05; **P < 0.005.