FIGURE 4.
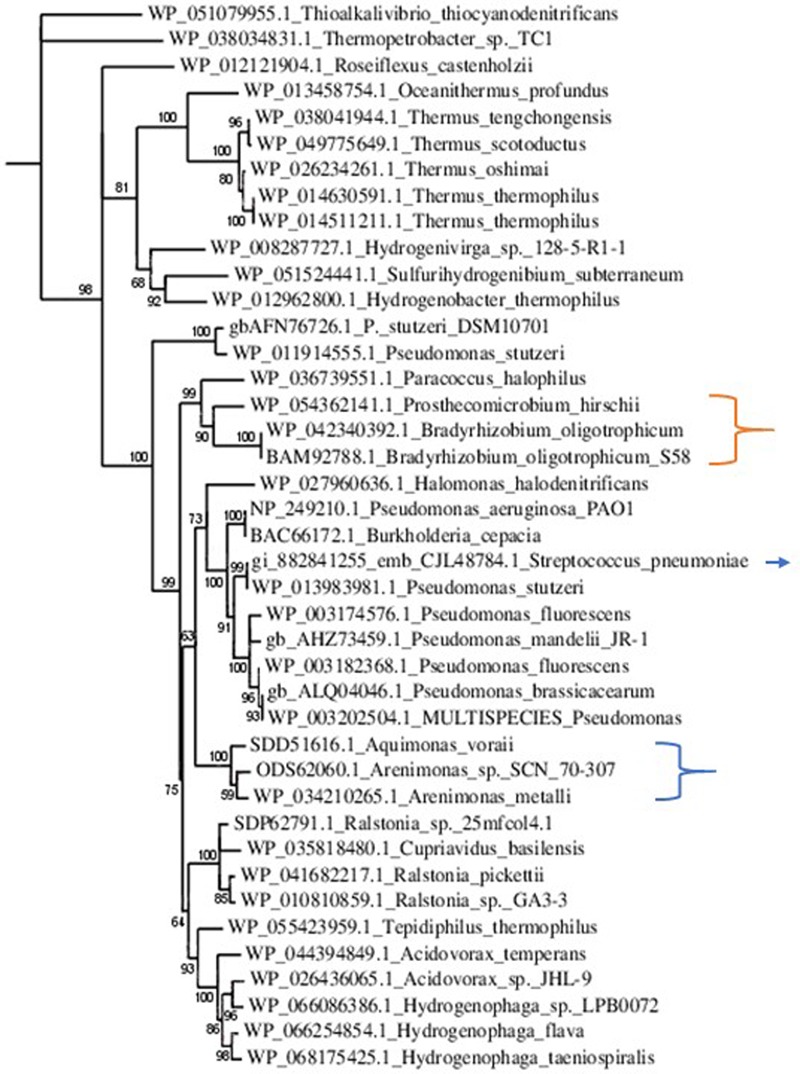
Phylogenetic tree of NirS sequences. Sequences were aligned with MUSCLE (v3.8.31) and ambiguous regions were removed with Gblocks (v0.91b). The phylogenetic tree was reconstructed using the maximum likelihood method implemented in the PhyML program (v3.1/3.0 aLRT). The substitution model considers that the data set does not contain invariable sites and assumes a 4-gamma-distributed rate category to account for rate heterogeneity across sites. The gamma shape parameter was estimated directly from the data (gamma = 0.998). Reliability for internal branch was assessed using the aLRT test (SH-Like). Graphical representation and edition of the phylogenetic tree were performed with TreeDyn (v198.3). Branches with a support value smaller than 50% were collapsed. The Gram-positive Streptococcus pneumoniae is indicated with an arrow. It is part of a cluster comprising Gram-negative phytopathogens and opportunistic pathogens. This result suggests the acquisition of nirS by horizontal gene transfer. The Rhizobiales cluster is indicated with an orange bracket. Although there were no homologs to NirS in Xanthomonas and Xylella, that is not the case for other Xanthomonadales, which are herein pointed out by the blue bracket.
