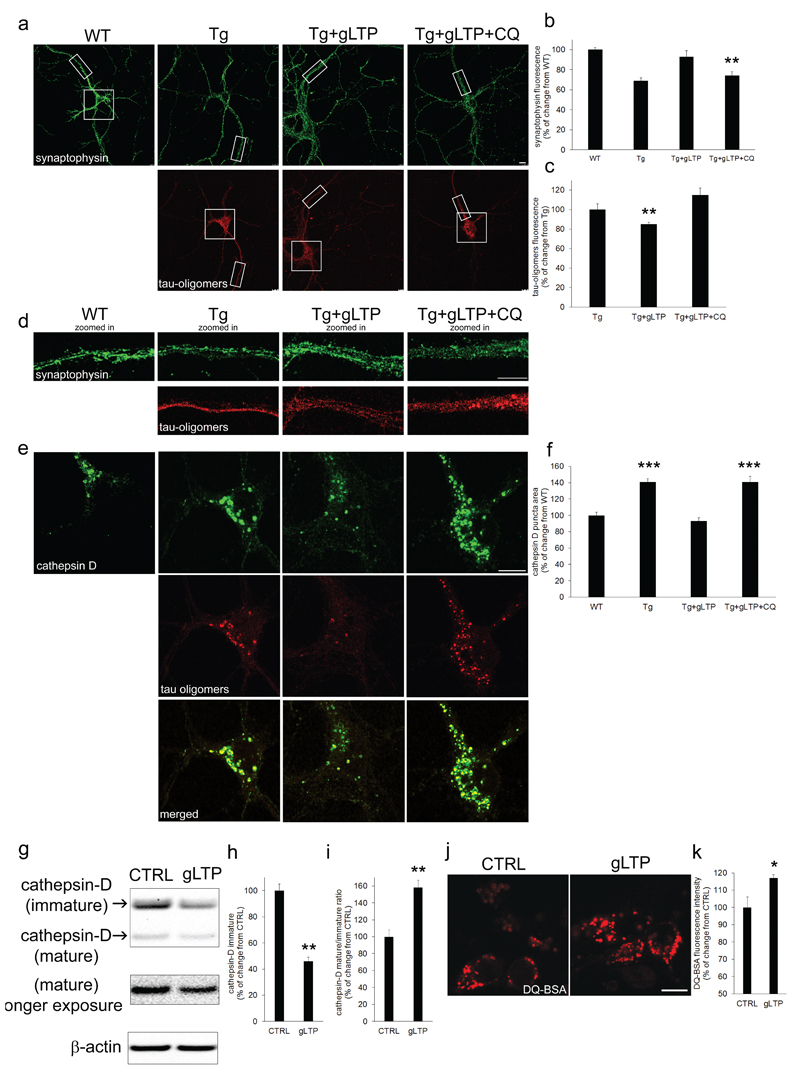
Figure 3. Tau oligomers accumulate in swollen lysosomes, and lysosomal activity is required for their gLTP-dependent clearance.
a-d Chloroquine (CQ) treatment prevented gLTP to reduce levels of Tau oligomers (lower panels), and to restore levels of synaptophysin (upper panels; scale bar 10μm) in Tg cultured neurons, as quantified by confocal immunofluorescence in c (n=5; one-way ANOVA test, p=0.0114; Tg+gLTP vs Tg+gLTP+CQ **p<0.01; Tg vs Tg+gLTP+CQ p>0.05) and b (one-way ANOVA test, p=0.0019; WT vs Tg+gLTP P>0.05; WT vs Tg+gLTP+CQ **p<0.01), respectively. e Zoomed-in of neuronal somas displayed in a: the size of lysosomes (upper panels; scale bar 10μm) is increased (41±4% of puncta area) in Tg compared to WT neurons, and Tau oligomers (middle panels) accumulated in enlarged lysosomes (merged images, bottom panels). f gLTP restored the size of lysosomes in Tg neurons back to WT; however, inhibition of lysosomal activity by CQ treatment prevented it. (n=5; one-way ANOVA test, p=0.0001; WT vs Tg ***p<0.001; Tg vs Tg+gLTP *** p<0.001; Tg+gLTP vs Tg+gLTP=CQ *** p<0.001). g-i Western blot analyses demonstrated a reduction (56±3%) of immature cathepsin D and an increase (58±9%) of the mature/immature cathepsin D ratio in gLTP compared to CTRL Tg neurons (n=5; two-tailed unpaired t-test, **p<0.01). j, k DQ-BSA assay to measure lysosomal function revealed a 17±2% increase of lysosomal activity in gLTP compared to CTRL neurons (n=5; two-tailed unpaired t-test, *p<0.05). “n” refers to a set of cultured neurons prepared from one mouse embryo. Two preparations of neurons were required and experiments were repeated accordingly.