Extended Data Fig. 3. LGR5 ECD reduces ISC/progenitors but not via apoptosis.
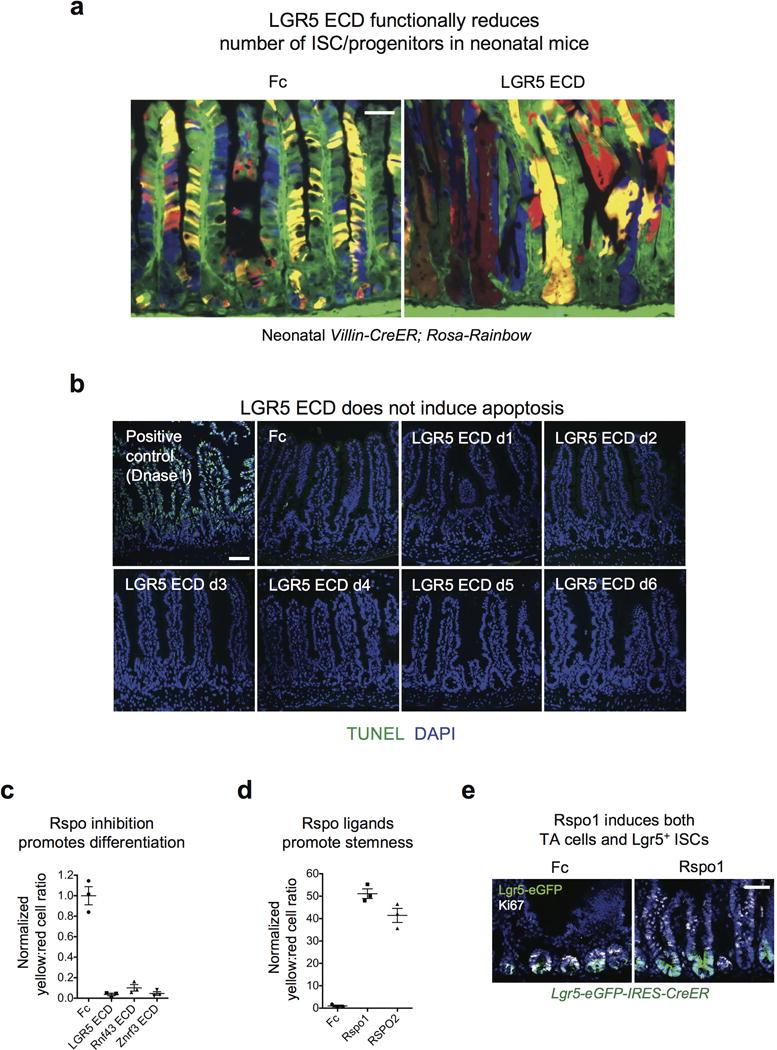
a, LGR5 ECD functionally reduces number of ISC/progenitors in neonatal mice. Multi-color clonal labeling of intestinal epithelial cells in jejunum of neonatal Villin-CreER; Rosa26-Rainbow mice, 8 days post-tamoxifen induction resulting in stochastic clonal labeling to one of four fluorescent colors and 7 days post-infection with Ad LGR5 ECD compared to control Ad Fc. Ad LGR5 ECD induced premature crypt monoclonality, reflecting a functional decrease in the number of clones functioning to repopulate the epithelium under conditions of Rspo inhibition, consistent with a marked reduction in ISC/progenitor number. Bars = 50 mm. b, LGR5 ECD does not induce apoptosis. TUNEL staining of jejunum at the indicated days after single i.v. injection of Ad LGR5 ECD into mice reveals absence of crypt apoptosis. Positive control TUNEL staining after DNase I treatment of sections is also shown. Bar = 50 mm. c, FACS quantitation of yellow:red (Lgr5+ ISC:differentiated) cell ratio from Fig. 2a. Error bars represent S.E.M. d, FACS quantitation of yellow:red (Lgr5+ ISC:differentiated) cell ratio from Fig. 2d, d4 post-treatment. Error bars represent S.E.M. e, Ad Rspo1 expands both Lgr5+ ISCs and Lgr5− Ki67+ proliferative crypt cells consistent with ISC and TA expansion. Bar = 50 mm.
