Extended Data Fig. 5. Wnt analog scFv-DKK1c functions via Fzd receptors to support Lgr5+ ISCs and can substitute for endogenous Wnts.
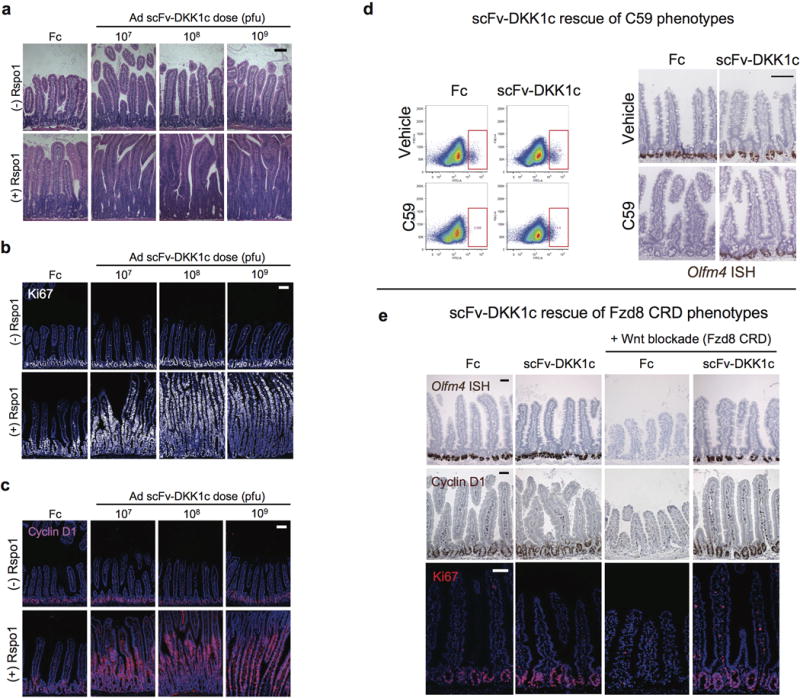
a–c, Dose-dependent effects of Ad scFv-DKK1c +/− Ad Rspo1 on the intestinal epithelium. H&E of jejunum on d4 post-adenovirus treatment (a). Mice were treated with adenovirus titers of 107 to 109 pfu. Ki67+ proliferation of jejunum on d4 after adenovirus injection (b). Dose-dependent effects of scFv-DKK1c on Wnt target gene cyclin D1 (c). Jejunum, IF, d4 post-adenovirus. Bars = 100 mm. d, Wnt analog scFv-DKK1c functionally substitutes for endogenous Wnts in vivo to rescue Lgr5+ ISC from C59-mediated loss. Loss of Lgr5-eGFP reporter signal (red box) by FACS analysis (left) and Olfm4 expression (right) from jejunum of mice treated with the small molecule Porcn inhibitor C59. Adenoviral overexpression of scFv-DKK1c prevents C59-mediated ablation of the reporter signal. Mice were treated with C59 for a total of 4 days that began 2 days following adenovirus injection. Bar = 100 mm. e, Wnt analog scFv-DKK1c rescues in vivo phenotypes elicited by the Wnt antagonist Fzd8 CRD. Ad Fzd8 CRD-mediated loss of Olfm4 (top), Wnt target gene CD44 (middle) and Ki67+ crypt proliferation (bottom) are rescued by concomitant adenoviral overexpression of scFv-DKK1c. Jejunum, d4 following treatment with adenovirus. Bars = 50 mm.
