FIGURE 7.
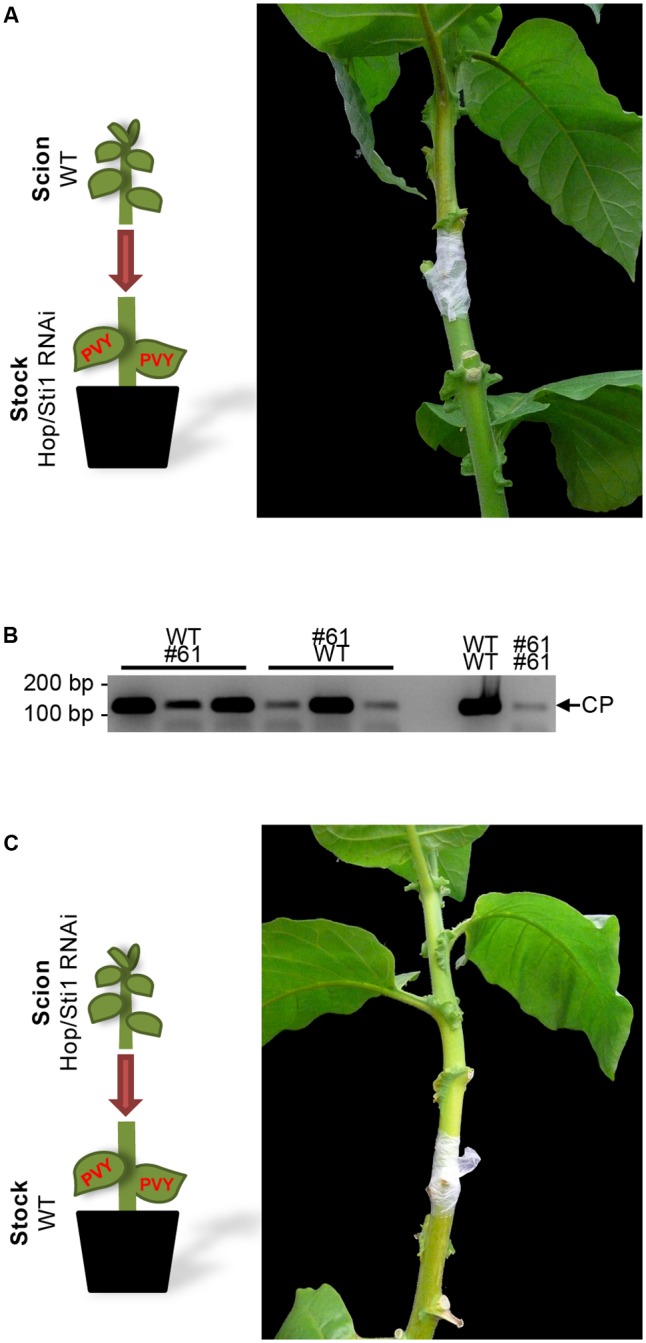
Reciprocal grafting of wild-type and Hop/Sti1-RNAi plants. (A) A wild-type scion was grafted on a PVYN-infected Hop/Sti1-RNAi rootstock. Two weeks after grafting, the wild-type type scion displayed infection symptoms. (B) Accumulation of viral RNA in scions of grafted wild-type and Hop/Sti1-RNAi plants, samples taken 2 weeks after grafting. RT-PCR was used to amplify a 122-basepair fragment of the viral RNA encoding the coat protein (depicted by an arrow labeled CP). Grafting combinations are labeled as scion over infected rootstock. Viral RNA could be detected in all tested mixed grafts (left) as well as in control plants (right, wild-type scion on infected wild-type rootstock, analogous for transgenic line #61). (C) Hop/Sti1-RNAi scion grafted on infected wild-type rootstock. Two weeks after grafting, the transgenic scion was still symptom-free, although viral RNA was detectable (compare to B).
