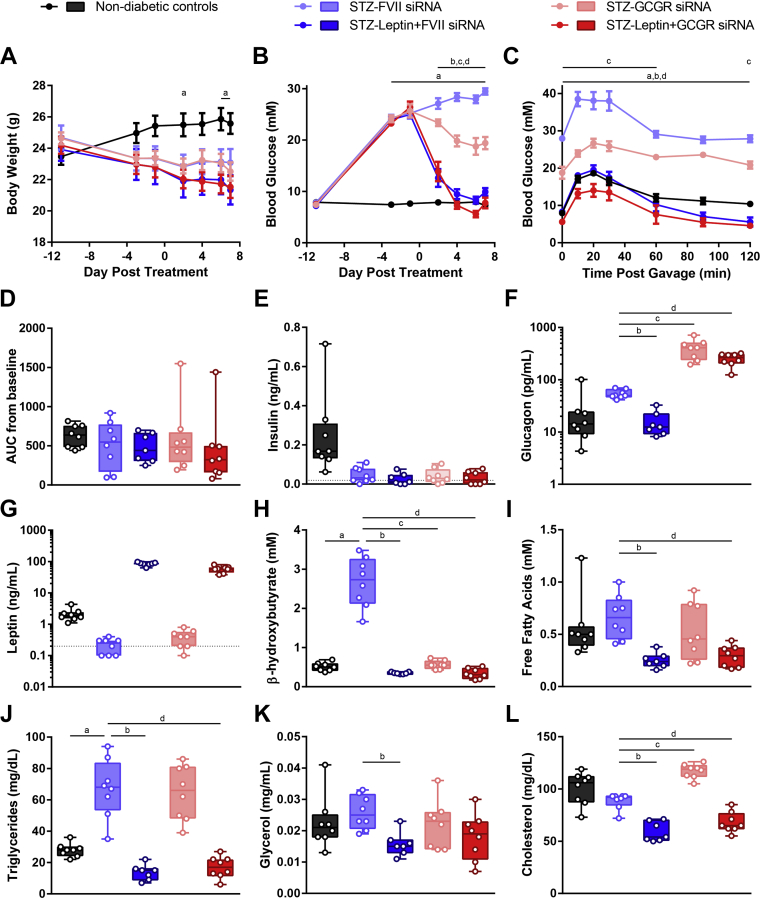
Figure 2.
Effect of leptin or 5 mg/kg Gcgr siRNA on glucose and lipid metabolism in STZ-diabetic mice. Insulin deficient diabetes was induced in mice by injecting 180 mg/kg STZ on day −11; vehicle was administered to non-diabetic controls. STZ-diabetic mice were treated with either FVII siRNA, Gcgr siRNA, FVII siRNA + leptin, or Gcgr siRNA + leptin on day 0. siRNA was delivered at a dose of 5 mg/kg via tail-vein injection and leptin was administered at a dose of 20 μg/day via mini-osmotic pump. Body weight (A) and blood glucose (B) were measured throughout the study. On day 6, an oral glucose tolerance test was performed using 1.5 g/kg of 30% dextrose (C), and area under the curve (AUC) from baseline was calculated (D). Plasma levels of insulin (E), glucagon (F), leptin (G), β-hydroxybutyrate (H), fatty acids (I), triglycerides (J), glycerol (K), and cholesterol (L) were analyzed on day 7. Each group was compared to the FVII siRNA treated group by 1- or 2-way ANOVA with Dunnett post-hoc testing; a, P < 0.05 non-diabetic controls vs FVII siRNA; b, P < 0.05 Leptin + FVII siRNA vs FVII siRNA; c, P < 0.05 Gcgr siRNA vs FVII siRNA; d, P < 0.05 Leptin + Gcgr siRNA vs FVII siRNA. Statistical analysis was not performed on insulin (E) or leptin (G) measurements as some samples were below the limits of detection, denoted by the dotted lines. In addition, five samples had insulin measurements too low to be interpolated and were assigned a value of 0. Data are mean ± SEM (A–C) or min to max box and whisker plots (D–K), n = 7–8.