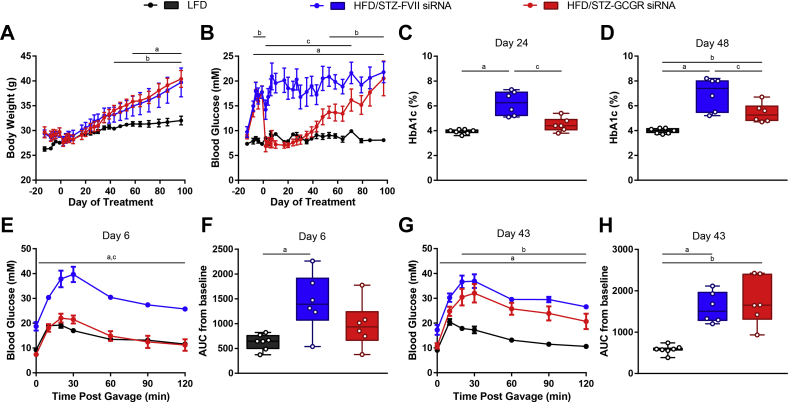
Figure 7.
A single injection of 10 mg/kg Gcgr siRNA reduces blood glucose for 2 months and improves oral glucose tolerance in HFD/STZ-diabetic mice. Mice on a HFD were injected with 100 mg/kg STZ on day −13. HFD/STZ-diabetic mice were treated with FVII siRNA or Gcgr siRNA at a dose of 10 mg/kg on day 0 and compared to untreated LFD fed mice. Body weight (A) and blood glucose (B) were measured throughout the study. HbA1c was analyzed on day 24 (C) and 48 (D). On day 6, an oral glucose tolerance test was performed using 1.5 g/kg of 30% dextrose (E), and area under the curve (AUC) from baseline was calculated (F). On day 43, an oral glucose tolerance test was performed using 1.5 g/kg of 30% dextrose (G), and area under the curve (AUC) was calculated (H). Groups were compared using a 1- or 2-way ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc testing; a, P < 0.05 LFD vs FVII siRNA; b, P < 0.05 LFD vs Gcgr siRNA; c, P < 0.05 FVII siRNA vs Gcgr siRNA. Data are mean ± SEM (A, B, E, G) or min to max box and whisker plots (C, D, F, H), n = 6–7.