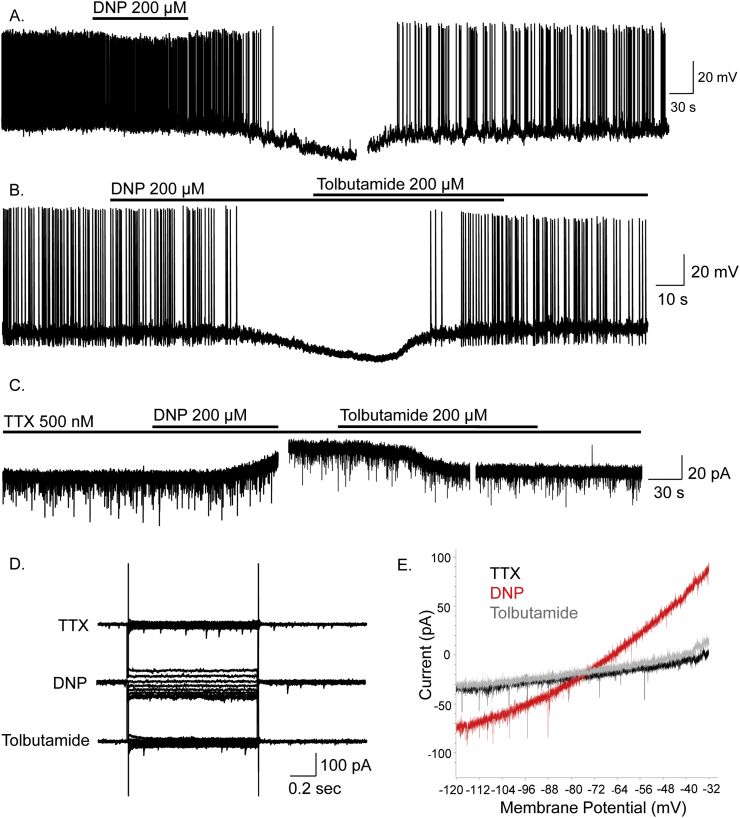
Figure 2.
DNP inhibits ARC NPY neurons via activation of KATP channels. (A) Whole-cell recordings showing DNP induced hyperpolarisation and inhibition of an NPY neuron. (B) DNP-induced inhibition was reversed by tolbutamide. (C) DNP-induced inhibition and associated outward current was reversed by tolbutamide and persisted in TTX indicating a direct post-synaptic effect via activation of KATP channels. (D) Voltage-clamp recordings in TTX showing current-voltage relations in control, DNP and tolbutamide. (E) Current responses to voltage-clamp ramps (8 mV/s from −120 to −30 mV; Vhold −60 mV) for control (black), DNP (red) and tolbutamide (grey), all in the presence of TTX. These data indicate DNP induced inhibition of NPY neurons is via activation of KATP.