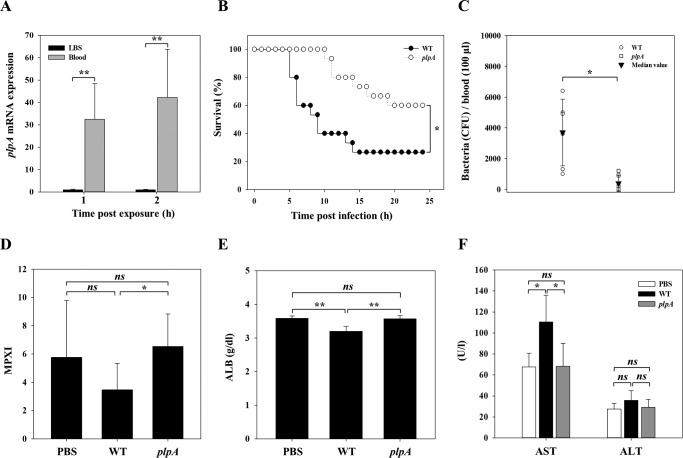
Figure 2.
VvPlpA is essential for pathogenesis of V. vulnificus. A, the wild type grown to an A600 of 0.5 was exposed to either LBS or blood of uninfected mice (n = 3) for 1 or 2 h and then used to isolate total RNAs. The plpA mRNA was determined by real-time qPCR analyses, and the plpA mRNA level in the bacteria exposed to LBS was set as 1. B, 7-week-old female ICR mice (n = 15 per group), injected intraperitoneally with iron-dextran, were intragastrically infected with the wild type and plpA mutant at doses of 108 cfu. C–F, the mice, without an iron-dextran administration, were intraperitoneally infected with the wild type (n = 11), plpA mutant (n = 11), or PBS (n = 5, control) at doses of 106 cfu and then sacrificed to obtain blood at 4 h postinfection. C, the number of either the wild type or plpA mutant in the blood of infected mice (n = 6 per group) was enumerated as cfu/100 μl of blood. Each open symbol represents an individual mouse. Black-filled inverted triangles indicate median values. D–F, the levels of MPXI (D), ALB (E), and AST/ALT (F) in the wild type– or plpA mutant–infected or PBS-treated mice (n = 5 per group) were determined by hematological analyses. Error bars, S.D. Statistical significance was determined by Student's t test for A and C–F, and by log-rank test for B. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005; ns, not significant. WT, wild type; plpA, plpA mutant; PBS, control.