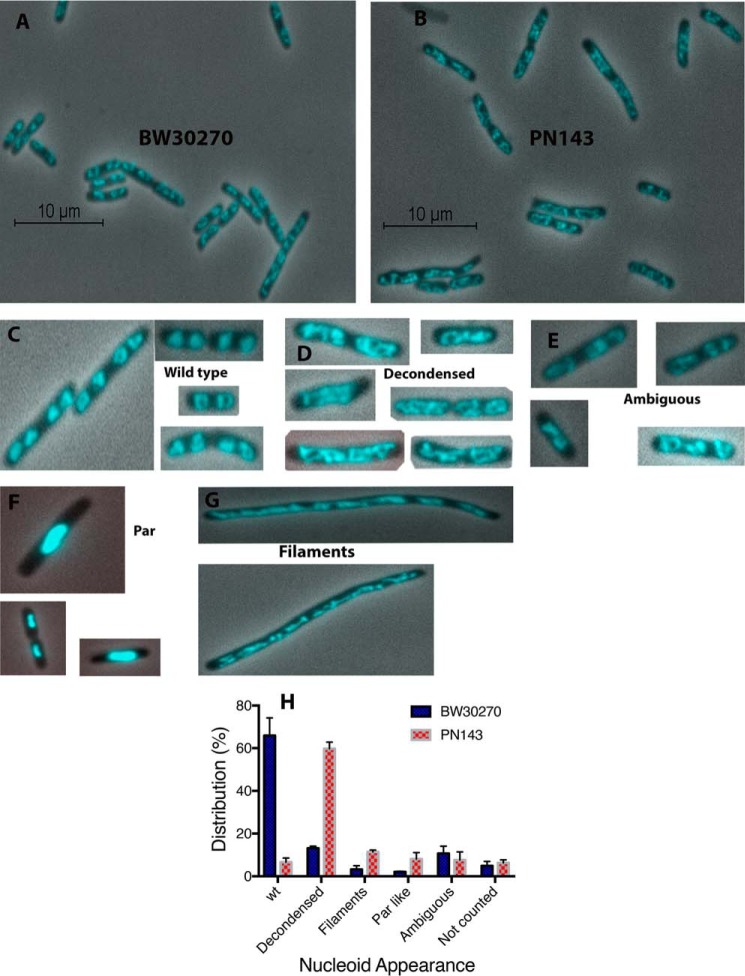
Figure 6.
MukB–Topo IV interaction is required for proper chromosome compaction in vivo. A and B, fields of wild-type (BW30270, A) and mukBD697KD745KE753K mutant (PN143, B) cells grown in LB medium to early log phase, stained with DAPI (cells were not fixed), spread on polylysine-coated slides, and imaged immediately. C--G, examples of nucleoid and cell types. C, cells with wild-type nucleoids. D, cells with decondensed nucleoids. E, cells where the state of the nucleoids was ambiguous. F, cells with par-like nucleoids. G, filamented cells. H, distribution of cells with different nucleoid types. Three laboratory members independently categorized cells for different nucleoid types. The same images were viewed by each laboratory member. About 500 cells were categorized from each of three independent experiments. Shown is the mean of the means. Not counted, cells that were either obscured because other cells lie across them or that were not completely in the frame of the image.