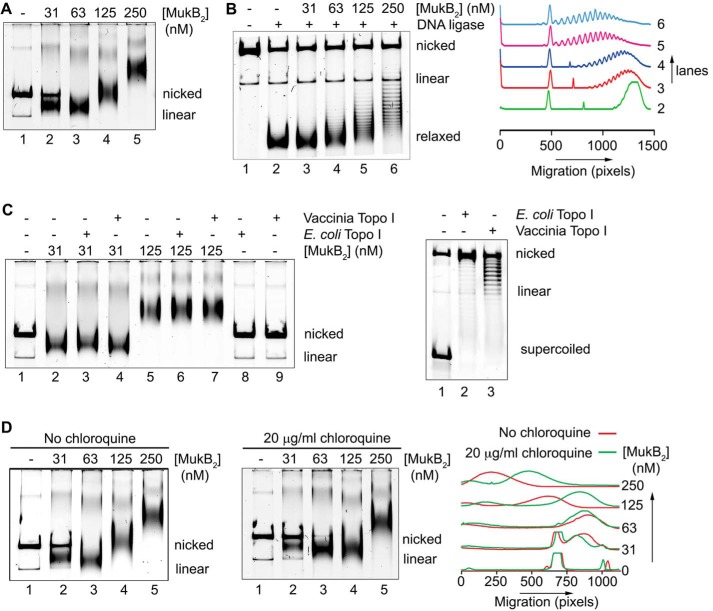
Figure 1.
MukB protects negative supercoils and stabilizes loop formation in DNA that is not constrained topologically. A, gel mobility shift analysis of MukB binding to DNA. MukB was incubated with the nicked DNA substrate for 5 min at 37 °C and then analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis as described under “Experimental procedures.” Nicked, nicked 11-kbp DNA substrate; Linear, linear form of the DNA substrate. B, MukB forms negative supercoils in the nicked DNA substrate. MukB, E. coli DNA ligase, and NAD were incubated with the nicked DNA substrate for 30 min at 37 °C. Left panel, products were deproteinized and then analyzed by electrophoresis through agarose gels containing 10 μg/ml chloroquine in both the gel and the running buffer as described under “Experimental procedures.” Right panel, densitometric lane traces of the gel shown in the left panel. C, MukB protects negative supercoils in the nicked DNA substrate. Left panel, MukB was incubated with the nicked DNA for 5 min at 37 °C. Either Vacinnia DNA topoiosmerase or E. coli DNA topoisomerase I were added to 3.1 and 6.2 nm, respectively, as indicated, and the incubation continued for 30 min. The products were then analyzed by gel electrophoresis as described in A above. Right panel, concentrations of topoisomerase (Topo) I used was more than sufficient to completely relax the supercoiled form of the plasmid in the absence of bound MukB. D, MukB stabilizes topologically isolated loops in the DNA. Left and middle panels, MukB was incubated with the nicked DNA substrate for 5 min at 37 °C and then analyzed by electrophoresis through agarose gels either in the absence or presence of 20 μg/ml chloroquine, respectively, in the gel and running buffer. Right panel, densitometric lane traces of the gels shown in the left and middle panels.