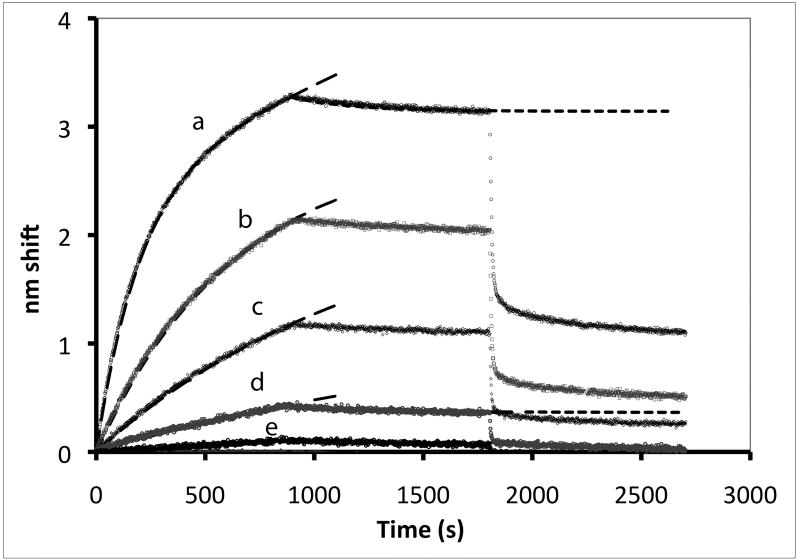
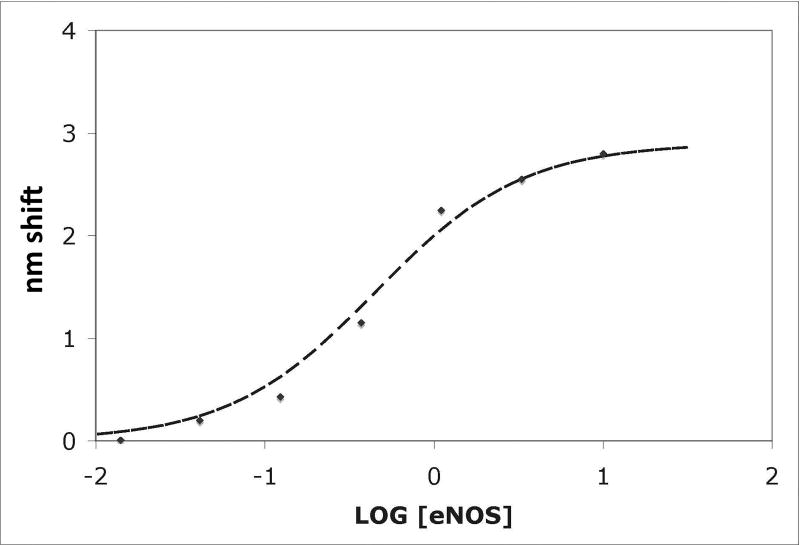
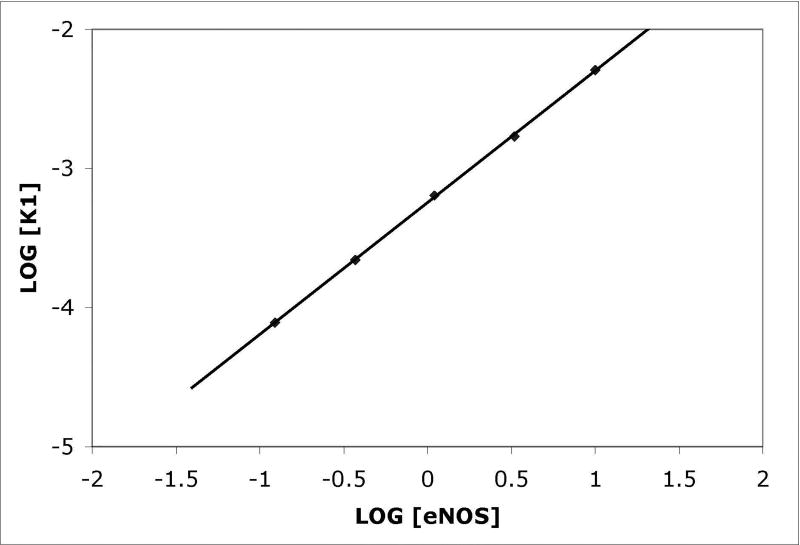
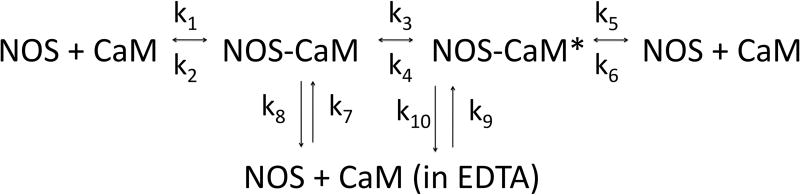
Figure 1. Binding of eNOS holoenzyme (analyte) to calmodulin tethered to sensor tips.
(A) NOS concentrations (top to bottom) were a:10 nM, b: 3.33 nM, c: 1.11 nM, d: 0.37 nM, and e: 0.123 nM; concentrations down to 0.005 nM were also examined. Binding was initiated by immersion of tips into solutions of eNOS at the concentrations listed; after 15 minutes, the tips were transferred into buffer containing calcium but no eNOS, and after 15 minutes of slow dissociation the tips were transferred into a solution of EDTA. A two exponential fit for binding is shown for the top trace, single exponential fits to early data for the others. For the physiologically relevant rapid phase, amplitudes were 2.8, 2.55, 2.25, and 1.15 and rate constants (kobs in sec−1) were 0.0051, 0.00185, 0.00084 and 0.00052. The rapid components account for most of the observed changes. The slow component in the top trace has an amplitude of 60 and rate of 0.00015 sec−1 when fit as an exponential; because the slow components are very slow, they can be fit as a line or as the slow conversion of the initial bound state into modified tightly bound states (see text). (B) Titration of signal intensity with eNOS showing rapid component amplitude vs [eNOS]. Sigmoidal titration simulation is shown with an apparent Kd of 0.65 nM. Plot of forward rate constant calculated from global fit of kobs vs. [eNOS] showing first order behavior with respect to eNOS. (D) Kinetics scheme showing steps for binding, dissociation and modification of components. Rate constants are: k1, forward rate constant for binding in Ca+2 buffer; k2, dissociation rate constant for binding in Ca+2 buffer k3, forward rate constant for conversion to slow release conformational state; k4, reverse rate constant conformational change; k5 and k6, forward and reverse rate constants for dissociation of the slow state in Ca+2 buffer (negligible), k7 and k8, forward and reverse rate constants for dissociation of the initial state in EDTA buffer; k9 and k10, forward and reverse rate constants for dissociation of the slow state in EDTA buffer.