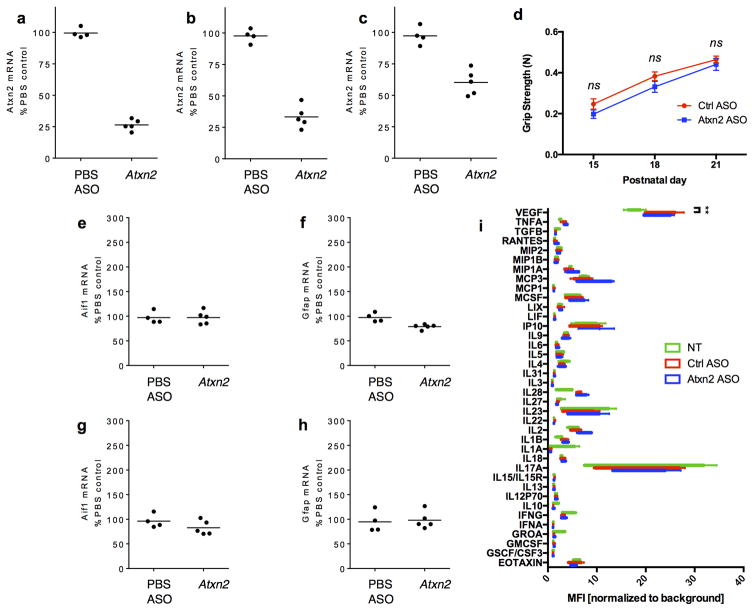
Extended Data Figure 7. An antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) targeting Atxn2 is able to successfully reduce mRNA levels throughout the central nervous system.
a) ICV injection at P1 of an ASO targeting Atxn2 was able to successfully reduce levels of Atxn2 mRNA in the spinal cord by ~75% when assessed at P28. Atxn2 reduction was also seen in the cortex (b) and cerebellum (c). d) Grip strength of WT mice was not effected by Ctrl or Atxn2 ASO injection (n = 16 per treatment). Mean and SEM plotted. Genetic markers of gliosis, Aif1 and Gfap, were not altered in the spinal cord (e, f) or cortex (g, h) after ASO injection. i) Using a Luminex 38-plex assay, we could not detect a significant difference in inflammatory markers among uninjected WT mice (n = 5) and WT mice treated with the Atxn2 (n = 4) or Ctrl (n = 5) ASOs (two-way ANOVA treatment group factor p = .32). However, the ASO treated animals had a small increase in 1 of the 38 markers, VEGF. Multiplicity-adjusted pairwise tests revealed that this difference was not significant for Atxn2 ASO treated mice (p = .17), but was for Ctrl ASO treated mice (p = .006). Min to max plotted. a–c,e–h) Biological replicates and means are plotted.