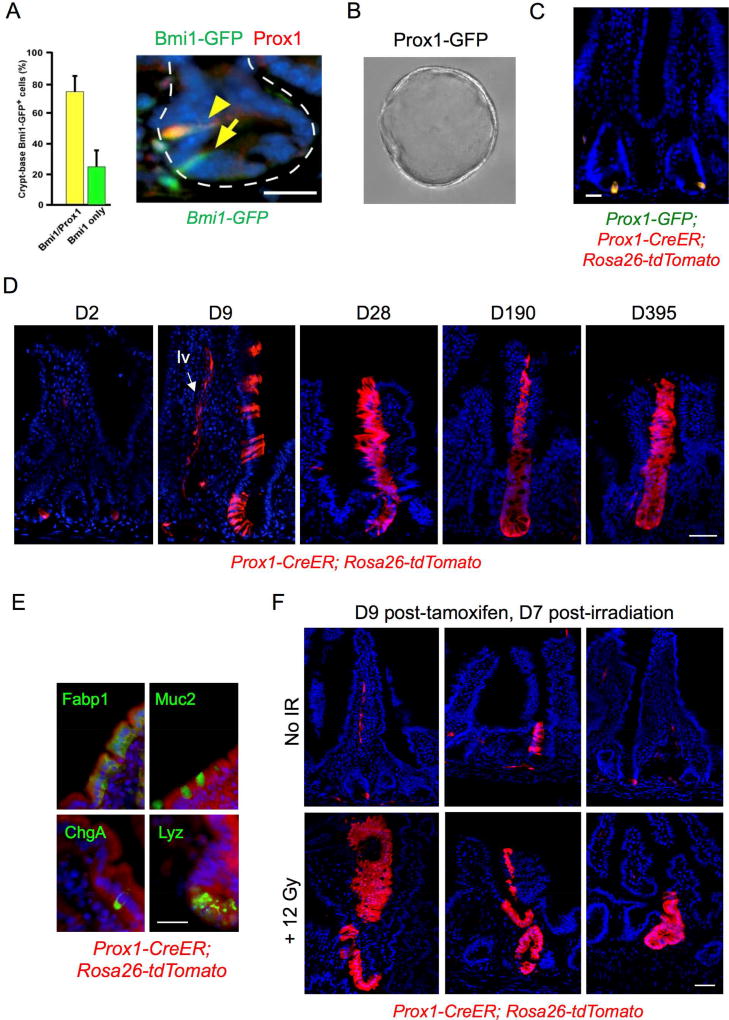
Figure 3. Functional similarities between Bmi1-GFP+ and Prox1+ cells in vivo.
A. Co-localization of Prox1 expression in 74.4% of Bmi1-GFP+ crypt cells by immunofluorescence, Bmi1-GFP (anti-GFP, green) and anti-Prox1 (red). Bar = 25 µm. Error bars indicate mean ± s.e.m. B. Clonogenic enteroid growth ex vivo from Prox1-GFP+ cells isolated from proximal jejunum, day 5. 20× magnification. C. Short-term (36h) in vivo tamoxifen-induced labeling of Prox1+ cells in jejunum of Prox1-GFP; Prox1-CreER; Rosa26 tdTomato mice marks crypt epithelial cells. Bar = 20 µm. D. Persistent lineage tracing in jejunum from a subset of crypt-based Prox1+ cells in tamoxifen-treated Prox1-CreER; Rosa26 tdTomato mice, 9 to 365 days after tamoxifen treatment. Lineage tracing was observed in approximately 1/150 crypts. Labeling was also observed in lymphatic vessels (“lv”, arrow) consistent with the known expression of Prox1 in lacteals and in ~10% of villi. Bar = 50 µm. E. Multi-potency of Prox1-expressing cells. Differentiation markers were detected by IF within Prox1 lineage stripes, with Fabp1 for enterocytes, Muc2 for goblet cells, ChgA for EE cells and Lyz for Paneth cells. Bar = 20 µm. F. Injury-inducibility of Prox1+ lineage traces in tamoxifen-treated Prox1-CreER; Rosa26 tdTomato mice. Tamoxifen was administered 2 days prior to delivery of 12 Gy whole body irradiation, followed by tissue harvest after an additional 7 days. Bar = 50 µm.