FIGURE 3.
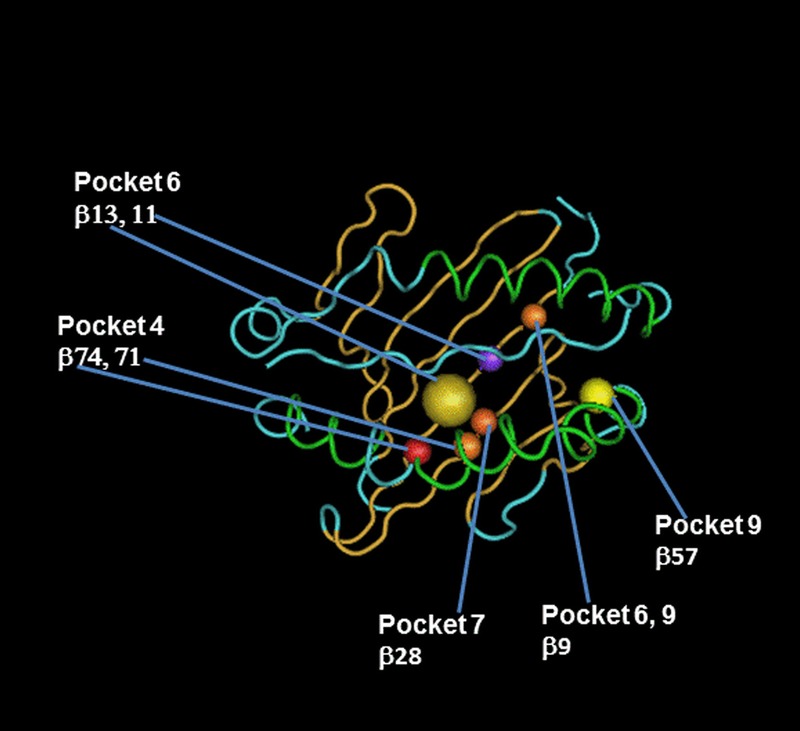
HLA-DRB1 AA substitutions in peptide-binding pockets account for the highest risk of GF attributable to HLA AA MMs. Figure illustrates the localization of HLA-DRB1 AA MMs found to be significantly associated with GF using a stepwise model as described in the Materials and Methods. AA sequences of HLA-DRB1 α and β chain are mapped onto a worm representation. AA mismatched sites of the HLA-DRB1 beta chain that account for the highest risk of GF attributable to HLA AA MM are labeled and numbered, with positions 71 and 74 occupying the P4 pocket, positions 11 and 13 occupying the P6 pocket, positions 28 occupying the P7 pocket, and position 57, occupying the P9 pocket. Arrows show these AA positions and pockets. A molecular model of the HLA-DRB1 α1β1 domain was derived by homology modeling from the 3D coordinates of HLA-DRB1*04 (Pdb_id 1:4MDJ_B and 4MDJ_A) with the bound peptide derived from Vimentin (Pdb_id 1:4MDJ_C).44 A worm representation model of AA sequences was produced using a Cn3D macromolecular structure viewer to view 3-dimensional structures from the NCBI's Entrez Structure database. (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/CN3D/cn3d.shtml). The functional and structural correlates of AA polymorphisms and interacting residue positions were based on a previously published report.2 Correlations plot of imputed HLA AA MMs for HLA-DRB1 was evaluated using a Pearson correlation between the probabilities of no MM at 1 position compared with the probability of no MM at another position using a sample size of 23,095 donor-recipient pairs from the cohort examined in this study. The observed highly correlated AA MM sites for each HLA- DRB1 locus is due to the well-known complex linkage disequilibrium patterns of the polymorphic AAs in the binding site of HLA class II molecule. R2 values of highly correlated HLA-DRB1 AA MM sites forming pockets 4, 6, 7, and 9 are listed below. Position 9 (pockets 6, 9) correlates with 10 [0.52], 11 (pocket 6) [0.62], and 13 (pocket 6) [0.52]. Position 13 (pocket 6) correlates with 9 (pockets 6, 9) [0.52], 10 [0.51], and 11 (pocket 6) [0.85]. Position 28 (pocket 7) correlates with 30 (peptide-contact) [0.75]. Position 57 (pocket 9) correlates with 14 (peptide contact) [0.57], 25 [0.57], 60 (TCR contact) [0.86], 74 (pocket 4) [0.56], 78 (peptide contact) [0.64]. Position 74 (pocket 4) correlates with 14 (peptide contact) [0.51], 25 [0.51], 57 (pocket 9) [0.56], 60 (TCR contact) [0.51], 73 (TCR contact) [0.63], and 78 (peptide contact) [0.53].
