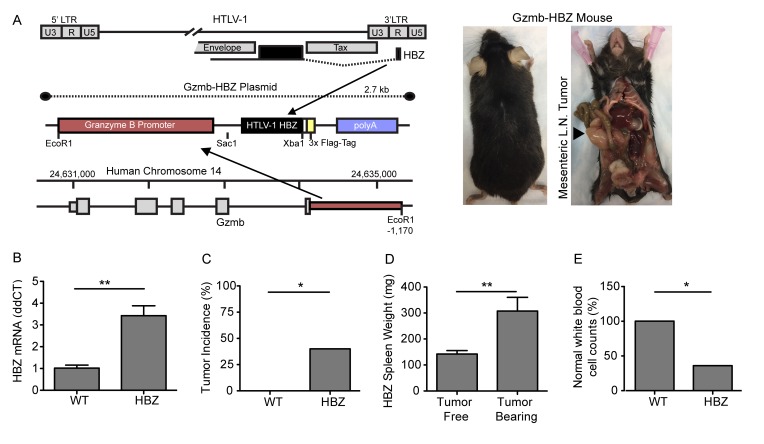
Figure 1. Granzyme B HBZ mice develop lymphoproliferative disease.
A. Granzyme B HBZ plasmid schematic and Gzmb-HBZ mouse. Arrow denotes a mesenchymal lymph node tumor in a Gzmb-HBZ mouse. B. HBZ mRNA expression in 4 month old WT and Gzmb-HBZ mice by Real-Time RT-PCR. C. Tumor incidence in 18-month WT and Gzmb-HBZ mice. D. Spleen weight in Gzmb-HBZ tumor free (n = 8) and tumor-bearing mice (n = 7). E. Percent of WT (n = 7) and Gzmb-HBZ (n = 15) mice with normal white blood cell counts (WBC). Normal WBC range was determined as the WT median +/- 2 standard deviations. B.-D. Statistical analysis represents mean +/- SEM. Statistical significance determined by non-parametric student’s t-test B., D. or Fisher’s exact test C., E. as appropriate. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001.