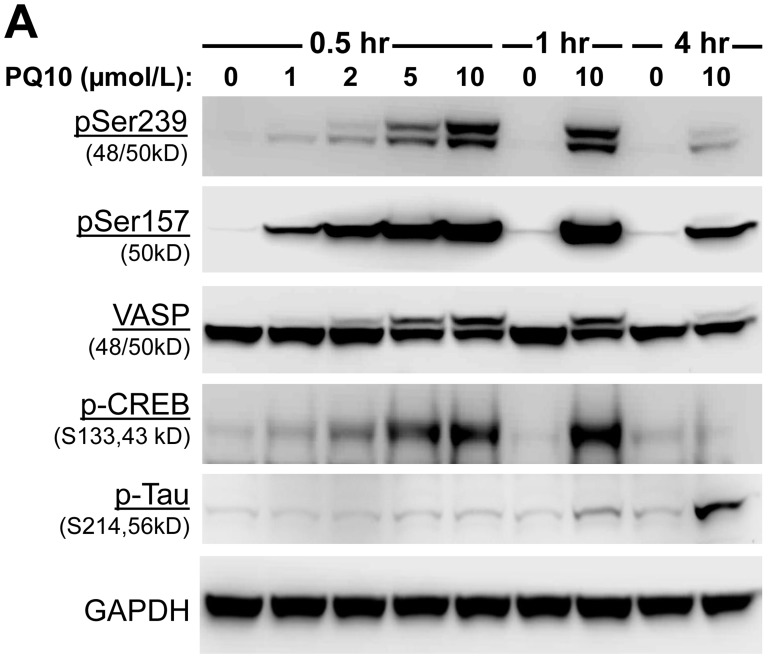
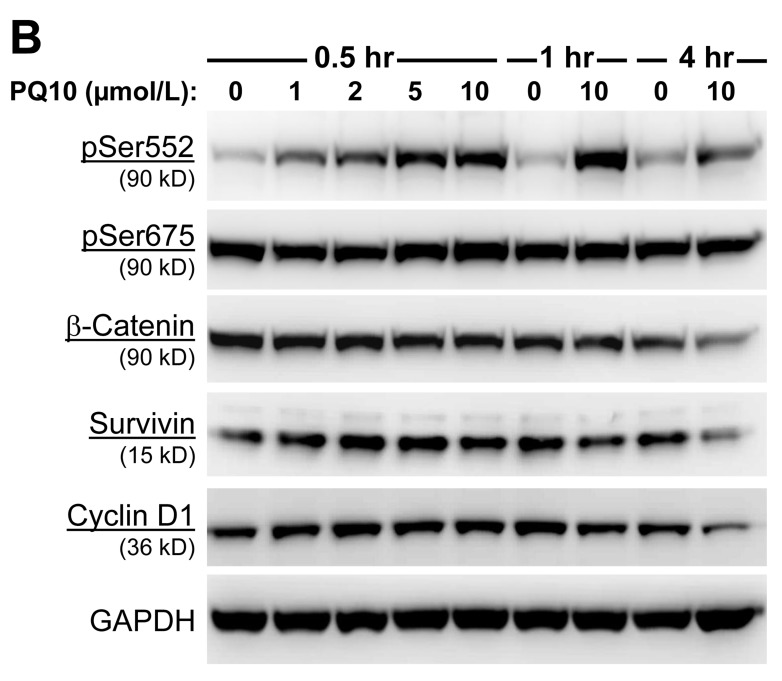
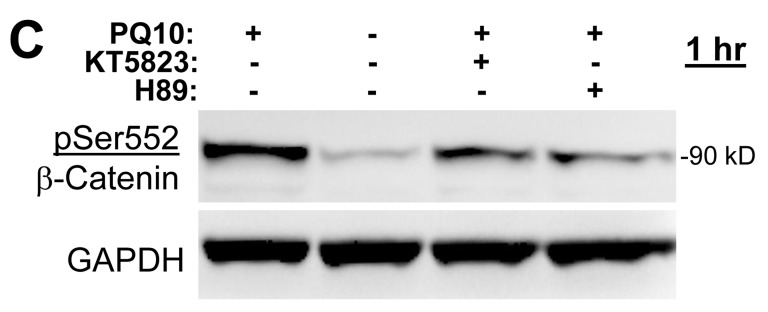
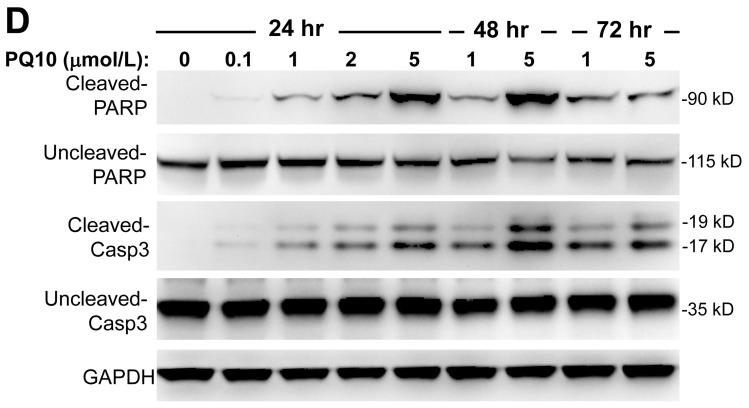
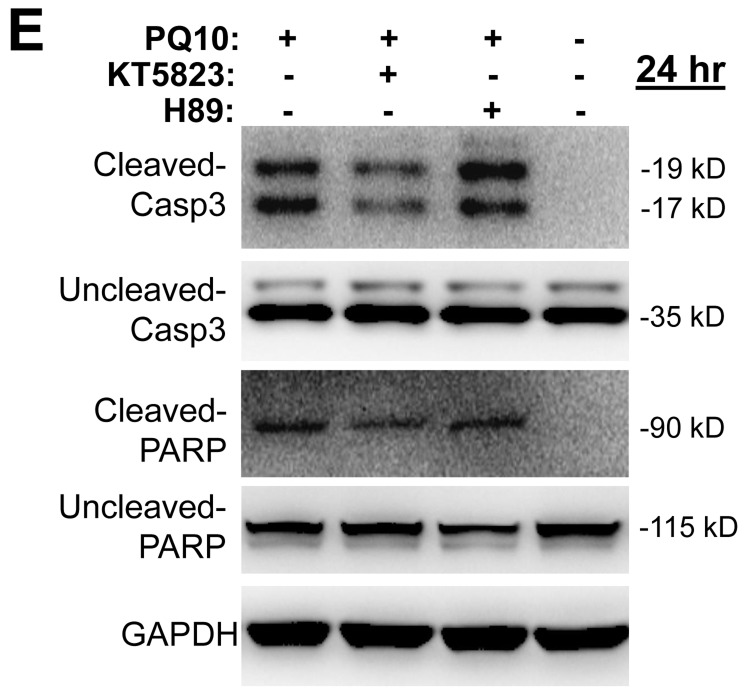
Figure 4. PQ10 activates PKG/PKA signaling, reduces β-catenin expression and induces apoptosis in NSCLC.
A. Site-specific phosphorylation of vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein, VASP (Ser157 and Ser259), cAMP response element-binding protein, CREB (Ser133), and microtubule-associated protein, Tau (Ser214) in H1299 cells were measured for concentration-dependent and time-related phosphorylation manners after PQ10 treatments. B. PQ10 initiated a phosphorylation of β-catenin at Ser552 but did not show a change at Ser675 after 0.5∼1 hour treatments. PQ10 also reduced total β-catenin, survivin and cyclin D1 expression after 4 hours of treatment. C. At 1 hour of treatment, PKG and PKA inhibitor, KT5823 (0.1 µmol/L) and H89 (1 µmol/L) showed partial inhibition of PQ10 (2 µmol/L) induced Ser552 phosphorylation of β-catenin. D. PQ10 induced apoptosis in H1299 NSCLC cells. The cleaved nuclear poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP) and caspase 3 (Casp3) proteins were detected by Western blotting after 24∼72 hours of treatment with different doses of PQ10. E. At 24 hours of treatment, PKG-inhibitor, KT5823, showed inhibition of PQ10 induced-cleaved Casp3 and PARP, but PKA-inhibitor H89 was ineffective.