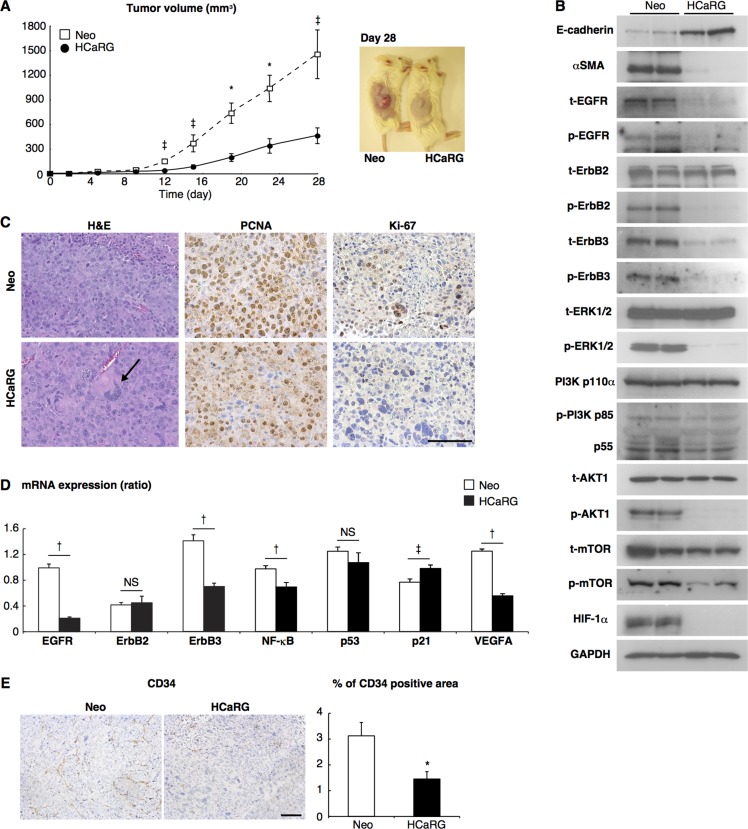
Figure 3. HCaRG inhibits tumor growth in a mouse homograft RCC model.
(A) Renca clones were implanted by subcutaneous injection (1 × 106 cells/mouse). HCaRG overexpression significantly inhibited tumor growth of homografted Renca cells as seen after 8 days. ‡P < 0.05, *P < 0.01. (B) Tumor lysates obtained 28 days after implantation were analyzed by western blot using appropriate antibodies. HCaRG overexpression led to more differentiated tumor cells in experimental RCCs, as indicated by more E-cadherin and less of αSMA compared to Neo-controls. Representative blots showed further that HCaRG suppresses EGFR and ErbB3. ErbB2 protein level was not changed by HCaRG overexpression, while its phosphorylation was diminished. The subsequent MAPK and PI3K/AKT pathways were inactivated in HCaRG-RCCs. (C) Representative images of H&E stain and immunostaining with two different proliferation markers, PCNA and Ki-67. HCaRG-RCCs showed less cell proliferation with increased multinucleated giant cells relative to Neo-RCCs. The black arrow indicates a multinucleated giant cell. Scale bars, 100 µm. (D) The mRNA expressions of ErbB receptors and their downstream genes were demonstrated by Real-Time PCR. ‡P < 0.05, †P < 0.005. NS, not significant. (E) Representative images and quantitative data of immunostaining with anti-CD34-antibody. HCaRG overexpression markedly decreased CD34-positive microvessels and endothelial cells in experimental RCCs at day 28. *P <0.01. Scale bars, 100 µm.