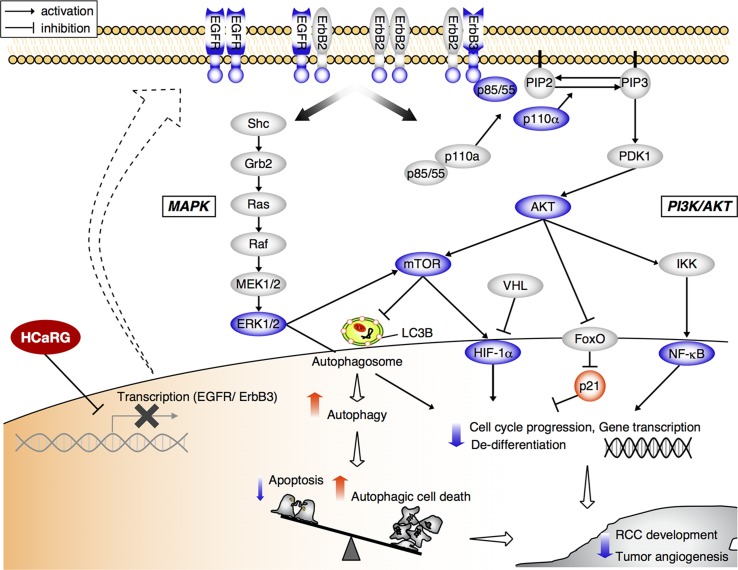
Figure 7. Scheme depicting the suppressive role of HCaRG in tumorigenic pathways of RCC.
Cancer cells overexpressing HCaRG show a more differentiated phenotype with lower cell proliferation than Neo-controls. HCaRG inhibits the phosphorylation of the proto-oncogene ErbB2 and inactivates subsequent MAPK and PI3K/AKT pathways by inducing the epigenetic gene silencing of EGFR and ErbB3 genes through their promoter methylation (Me). In addition, HCaRG facilitates programmed cell death by inducing autophagy via inactivation of AKT/mTOR pathway. As a result, tumor growth and angiogenesis of RCC are inhibited by HCaRG. The blue color indicates down-regulation or de-phosphorylation. The red color indicates up-regulation or activation.