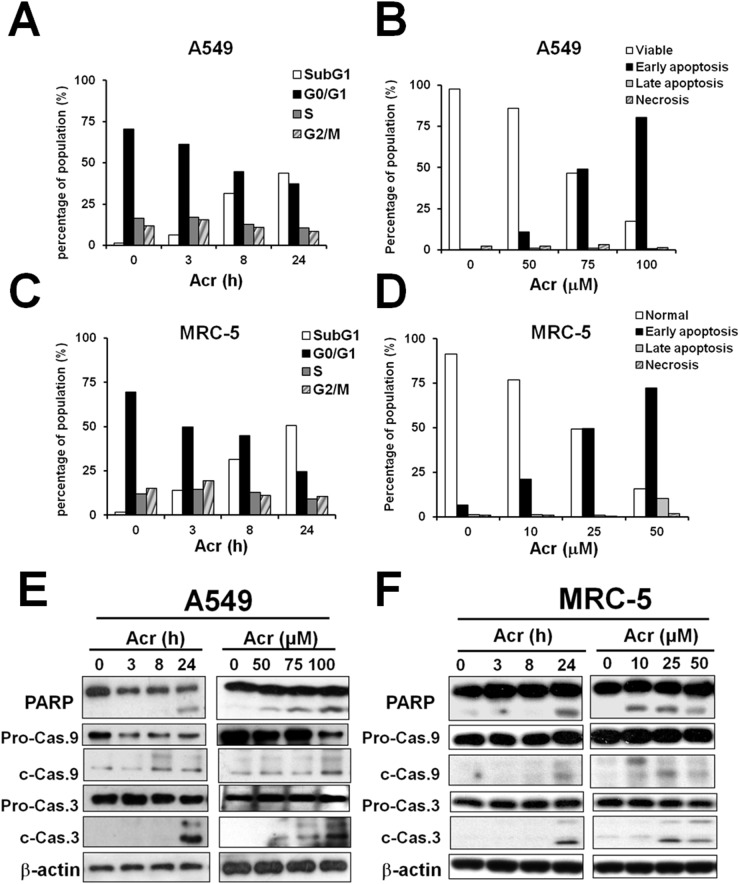
Figure 1. Acrolein-induced cytotoxicity occurs primarily via apoptosis.
Cells were treated with Acr (A549: 75 μM; MRC-5: 25 μM) for different times (0-24 h) or treated with different concentrations of Acr (A549: 0-100 μM; MRC-5: 0-50 μM), then incubated for 24 h. Panels (A & C) show cells in different cell cycle phases as determined by propidium iodide (PI) staining and flow cytometry analysis. Panels (B & D) show Acr induced apoptosis and necrosis as analyzed by Annexin V and PI staining and flow cytometry analysis. Panels (E & F) show Acr-induced cleavage of PARP, caspase 9 and caspase 3 in Acr-treated A549 or MRC-5 cells in Western blot analyses.