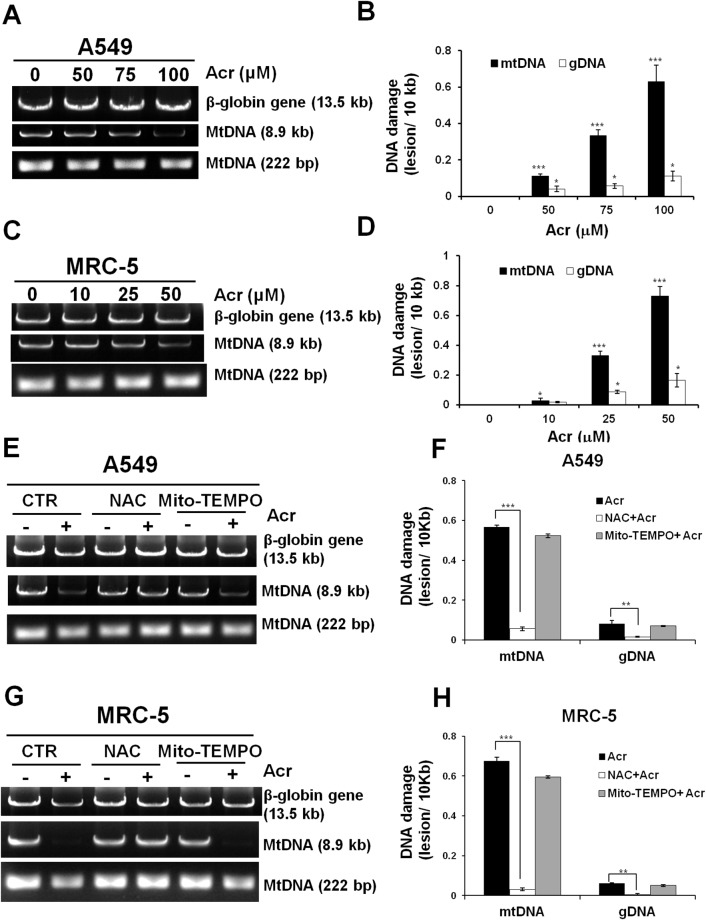
Figure 4. Acrolein induces more DNA damages/ unit length DNA in mtDNA than in nDNA.
In panels (A & C), cells were treated with Acr (A549: 0-100 μM, MRC-5: 0-50 μM for 6 h), DNA was extracted, following by QPCR with specific primers against mtDNA (8.9kb, 222bp) and nDNA (β-globin, 13.5kb). The resultant DNAs were separated by electrophoresis in a 1% agarose gel as previously described [67]. Panels (B & D) show quantifications of DNA damages in mtDNA and nDNA. In panels (E & G), cells were pretreated with NAC (5 mM) or Mito-TEMPO (100 μM) for 1 h followed by Acr treatment (A549: 100 μM, MRC-5: 50 μM) for 6 h. DNA damages in mtDNA and nDNA damages were analyzed, the same as described above. Panels (F & H) show quantifications of Acr-induced DNA damages in mtDNA and nDNA in cells pretreated with NAC (5 mM) or Mito-TEMPO (100 μM). Bar graphs show data collected from 3 independent experiments. Data are mean ± s.d. * P< 0.05; ** P<0.01; ***P<0.005.