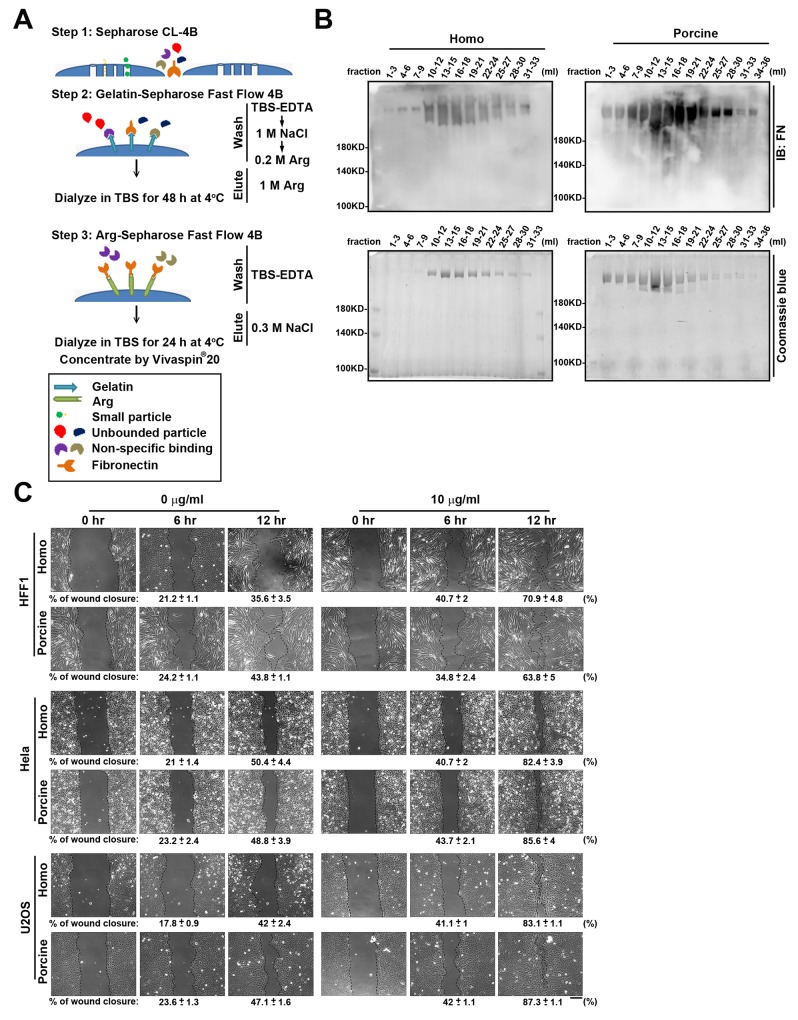
Figure 1. Fibronectin purification from homo and porcine plasma.
(A) Flow diagram of the purification steps used to isolate fibronectin from homo and porcine plasma. In step 1, cleared plasma was passed through a pre-column of Sepharose CL-4B in order to collect high molecular weight proteins. In step 2, the flow-through materials obtained from Sepharose CL-4B was loaded on a pre-column of gelatin-Sepharose Fast Flow 4B. After removing unbound proteins by sequentially washed with TBS-EDTA, 1 M NaCl and 0.2 M Arginine (Arg), the fibronectin was eluted with 1 M Arg and then dialyzed against TBS for 48 h at 4°C. In step 3, dialyzed material was applied to an Arg-Sepharose Fast Flow 4B column. After washing the column with TBS-EDTA, the fibronectin was eluted from the gel using 0.3 M NaCl/TBS-EDTA, and then dialyzed against TBS for 24 h at 4°C. Finally each of the fibronectins were concentrated using a Vivaspin 20 centrifugal concentrator (Molecular Weight Cut Off: 100 kDa). (B) The eluted fractions obtained from the Arg-Sepharose Fast Flow 4B column were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies against fibronectin (FN) and Coomassie blue staining. (C) HFF1, Hela and U2OS cells plated on 6-well plates coated with 0 and 10 μg/ml homo or porcine plasma fibronectin for 16 h were assayed for wound-healing migration, which was monitored by time-lapse microscopy. The still images were obtained at the indicated times after wounding. The dotted lines mark the edge of the wound at the 0-h, 6-h and 12-h time points of wound-healing migration. Bar, 200 μm. Bottom: the percentage of wound closure was calculated using Metamorph software. Data are mean ± s.e.m. (n = 5 independent experiments).