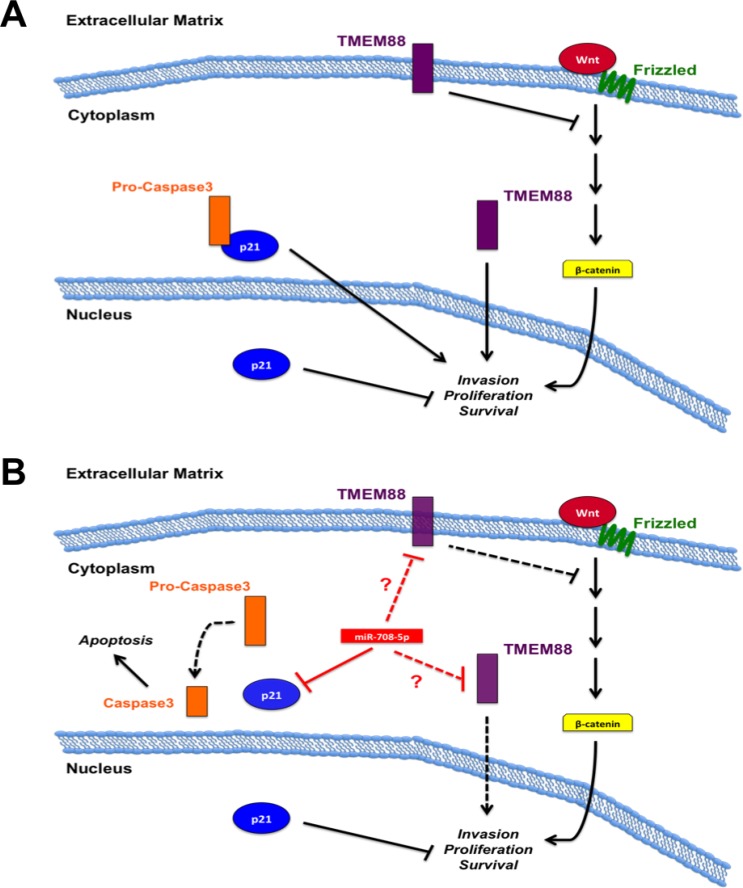
Figure 4. miR-708-5p model in lung cancer.
(A) TMEM88 and p21 oncogenic and tumor suppressive mechanisms in lung cancer. Membrane bound TMEM88 suppresses pro-oncogenic WNT signaling, while cytoplasmic TMEM88 promotes tumorigenesis. Cytoplasmic p21 sequesters pro-caspase 3 to hinder pro-apoptotic signaling while nuclear p21 acts as a tumor suppressort. (B) Function of miR-708-5p on TMEM88 and p21 signaling. miR-708-5p decreases cytoplasmic p21 levels while not altering nuclear p21 levels. Deregulation of pro-caspase 3 allows for apoptotic signaling to proceed, while nuclear p21’s tumor suppressive functions remain intact. miR-708-5p may directly or indirectly suppress TMEM88. If miR-708-5p represses membrane-bound TMEM88, regulation of WNT signaling is lost, resulting in increased pro-oncogenic signaling. miR-708-5p repression of pro-tumorigenic cytoplasmic TMEM88 would result in decreased invasion, proliferation, and survival. Black solid lines indicate activation (arrows) or suppression (blocks) while red lines indicate miR-708-5p direct (solid) or unknown (dotted, ?) targeting. Dotted black lines represent signaling inhibition.