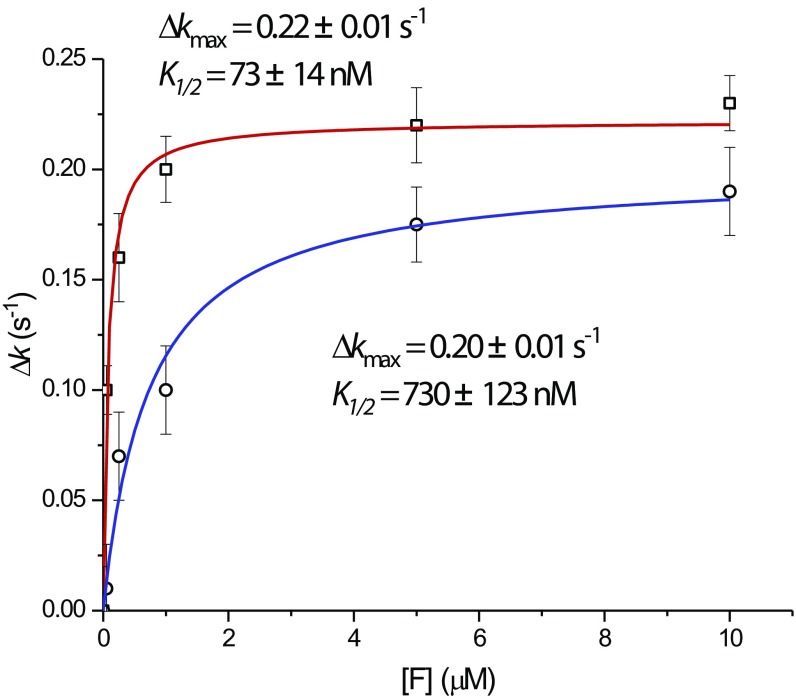
Fig. S5.
Fully modified (WT) and unmodified (K34A, EF-Pm) isoforms of EF-P have distinct capacities to rescue miscoding-stalled late intermediates of translocation. The plot shows the translocation rate difference of PRE complexes programmed with near-cognate AAU as a function of the concentration of the modified WT EF-P and mutant (K34A, EF-Pm). Δk = kEF-P − k0, where k0 = 0.11 s−1 (the rate of translocation observed in the absence of EF-P factors; Table 1). Data were well described by hyperbolic functions (Δk = Δkmax[F]/(K1/2 + [F]), where K1/2 is the factor concentration [F] at which the increment in the translocation rate is half its maximum) for both EF-P (□) and EF-Pm (○). Notably, the K1/2 of EF-Pm is 10.0 ± 2.6-fold higher than the K1/2 of WT EF-P. Translocation rates were calculated as described in Materials and Methods.