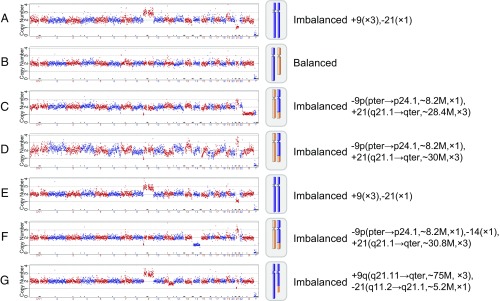
Fig. 3.
Chromosome ploidy results of the embryos from a patient (case no. 38744). In this clinical case, seven blastocyst embryos, A–G, were obtained and biopsied for chromosomal analysis. One embryo, B, was identified as having normal ploidy; the other six embryos were all type II embryos with abnormal Chrs 9 and 21. These abnormal embryos were used as reference embryos to identify the translocation breakpoint. The translocation breakpoint was identified at chr9:8,200 ± 200 kbp and chr21:19,600 ± 200 kbp with the consensus of the reference embryos. Subsequently, for each embryo, the SNPs flanking the breakpoint were examined, and then haplotype linkage analysis was performed. Detailed haplotype linkage analysis to resolve the translocation-carrier status of the embryos is illustrated in Fig. 4.