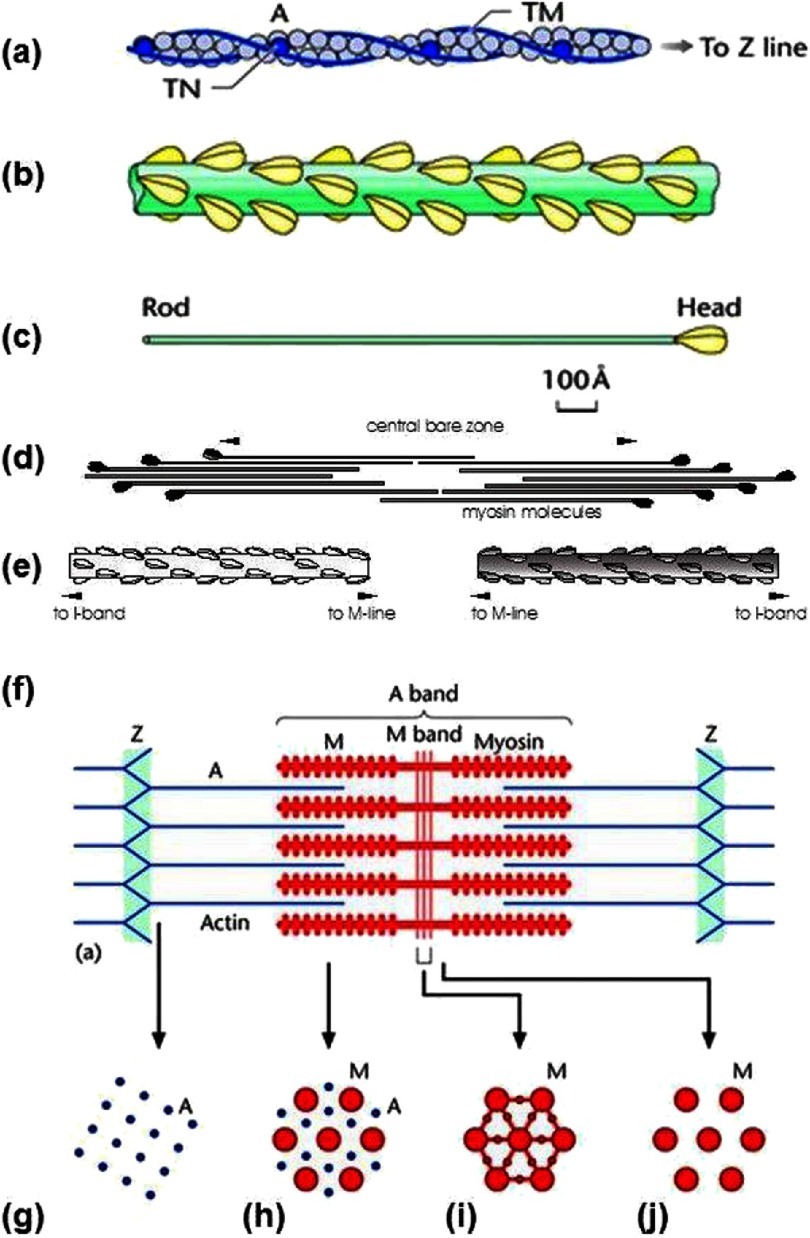
Figure 2. (a) Actin filament composed of actin molecules, A, two tropomyosin strands, TM, and troponin molecule complexes, TN.
(b) Bridge region of myosin filament composed of myosin molecules shown in (c) with the rod of the myosin molecules forming the backbone of the filament and the myosin heads arranged on the surface of the filament backbone. (d) The bipolar packing of the myosin molecules showing the anti-parallel arrangement giving rise to a heads-free bare zone region at the centre of the filament. This is also illustrated in (e). (f) Sarcomere structure extending between two successive Z-bands, M: Myosin, A: Actin. (g-j) Cross-sectional views through different parts of the sarcomere, showing (g) the square lattice of actin filaments in the I-band, (h) the hexagonal lattice between overlapping arrays of actin and myosin filaments in the A-band, (i,j) the hexagonal lattice of myosin filaments in the M-band (i) and bare-zone (j) regions, with the extra M- protein density linking the myosin filaments at the M-region in the centre of the sarcomere (i). (From Squire et al., 2005, with permission).