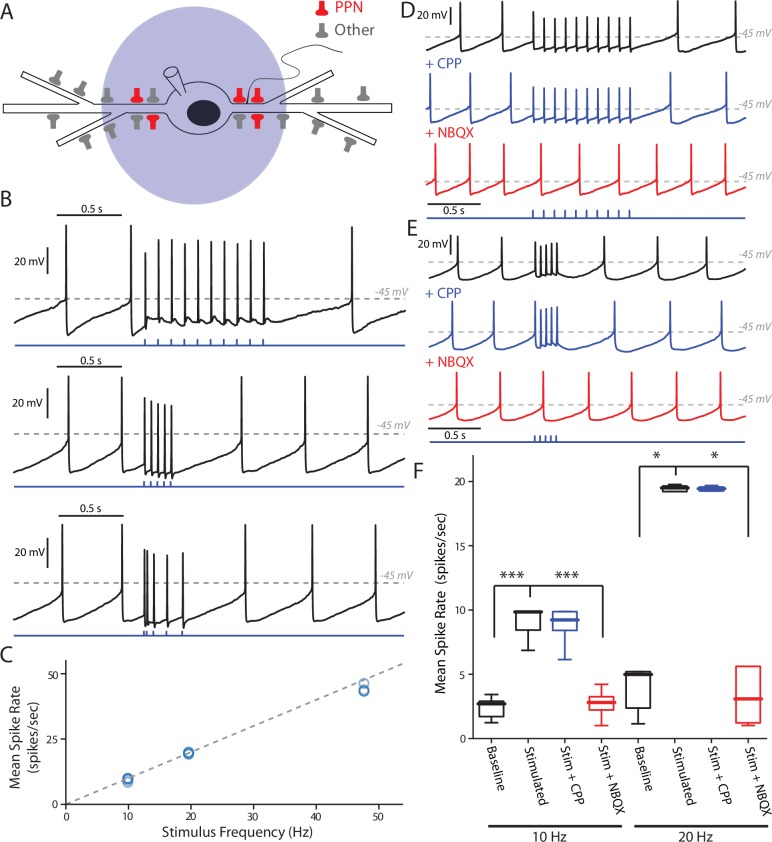
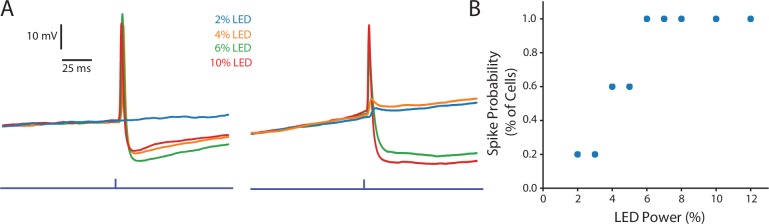
Figure 4. PPN glutamatergic input is capable of patterning SNc DA neuron firing.
(A) Full field blue-LED stimulation of ChR2-expressing PPN afferents was performed while recording spiking activity in SNc DA neurons using the perforated-patch configuration. (B) Example traces of different stimulation patterns: (Top) 10, 1 ms stimuli with an inter-stimulus interval of 100 ms, (Middle) 5, 1 ms stimuli with an inter-stimulus interval of 50 ms, and (Bottom) 5, 1 ms stimuli with inter-stimulus intervals of 20 ms, 50 ms, 100 ms, and 12 0 ms. In all cases spikes were reliably generated by the stimulation protocols. (C) Summary of the mean intra-stimulus spike frequency (spikes/s) as a function of the frequency of stimulation. The measured spike frequency was linearly related to the stimulation frequency in a near 1:1 relationship. (D) Example traces from a SNc DA neuron responding to the 10 stimuli, 10 Hz PPN ChR2 stimulation protocol before and after pharmacological manipulation. Application of the NMDAR antagonist, CPP (5 μM), did not significantly attenuate the response to PPN stimulation, while application of the AMPA receptor antagonist, NBQX (10 μM) completely abolished the evoked response. (E) Similar to (D), with the primary difference being the usage of the 5 stimuli, 20 Hz PPN stimulation protocol. As with (D), application of CPP failed to attenuate the response, while NBQX completely abolished the response. (F) Summary of pharmacological manipulation of SNc DA neuron firing pattern response to PPN stimulation. Both 10 Hz (9.03 ± 1.19 spikes/s, n = 9) and 20 Hz (19.53 ± 0.25 spikes/s, n = 5) stimulation significantly increased firing rate in comparison to control (10 Hz stim: 2.40 ± 0.82 spikes/s, n = 9, p=0.0001; 20 Hz stim: 3.43 ± 1.90 spikes/s, n = 5, p=0.0117). CPP application failed to significantly decrease the response to stimulation (10 Hz stim: 8.81 ± 1.55 spikes/s, n = 5, p=0.8413; 20 Hz stim: 19.49 ± 0.19 spikes/s, n = 5, p=1.0). In contrast, NBQX application significantly attenuated the PPN evoked response (10 Hz stim: 2.71 ± 1.10 spikes/s, n = 6, p=0.0008; 20 Hz stim: 2.73 ± 2.25 spikes/s, n = 5, p=0.0234). Summaries are presented as mean ± standard deviation. Statistical tests used were two-tailed Mann-Whitney tests with Holm-Bonferroni corrections for multiple comparisons. ***p<0.001, *p<0.05.