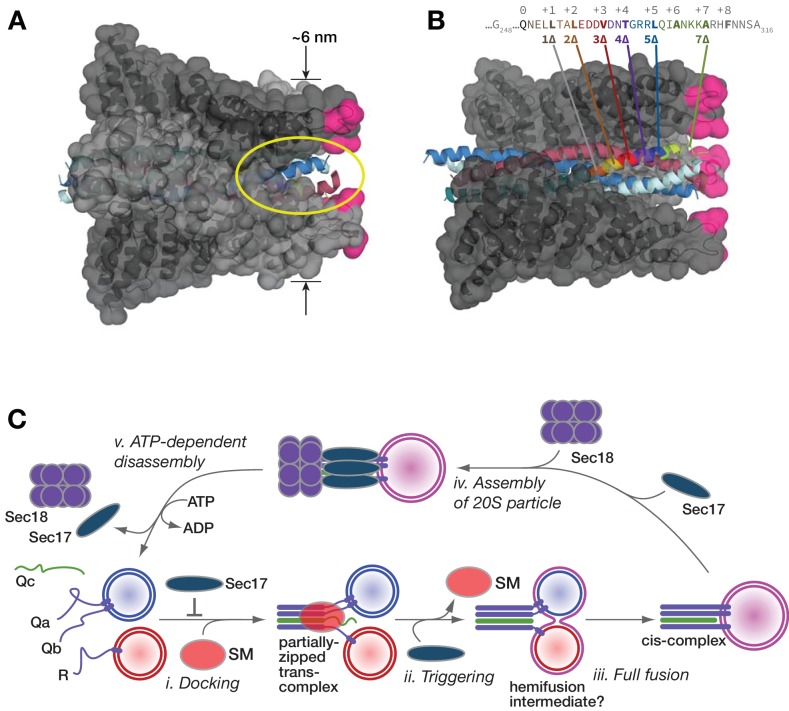
Figure 11. Working model.
(A and B) Sec17/α-SNAP on quaternary SNARE complex (renderings based on PDB 3J96; (Zhao et al., 2015). In B, note the tapered overall shape of the SNARE-Sec17 complex, which forms a roughly triangular structure that could fit between two docked membranes bearing partially zipped SNARE complexes. The hydrophobic loop is magenta. The yellow ellipse shows one of four portals between adjacent Sec17 molecules, through which unstructured SNARE juxta-membrane regions could pass when SNAREs are complexed in the trans configuration. In C, one of four Sec17 molecules is omitted to reveal the Qc packing layers. The portal openings begin at approximately layer +6. Sec17 partially contacts the SNAREs to layer +7 or +8. (C) Interplay of Sec17 and SM-tethering complex on the forward fusion pathway. The early inhibitory function of Sec17 is likely to involve sequestration of SNAREs or SNARE complexes prior to the onset of trans-SNARE interactions. This early inhibition is suppressed by the SM (in our experiments, HOPS-Vps33). The late, stimulatory function of Sec17 can occur in either the absence or presence of HOPS/Vps33. When HOPS-Vps33 is present, Vps33 (SM) ejection from the SNARE complex is a prerequisite for completion of C-terminal SNARE zippering and fusion.