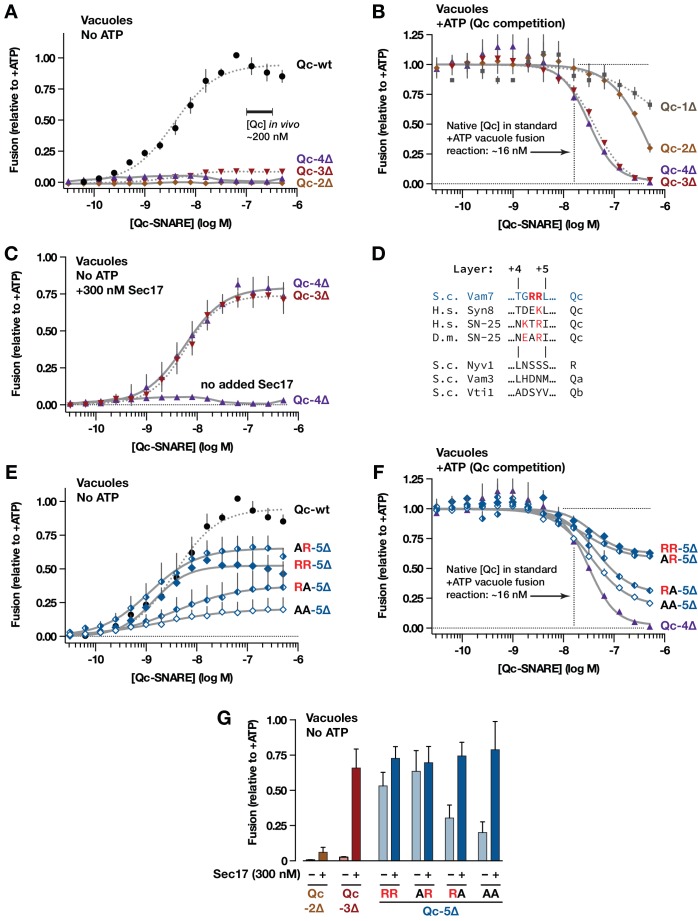
Figure 3. Interplay of SNARE zippering and Sec17 in cell-free assays of homotypic vacuole fusion.
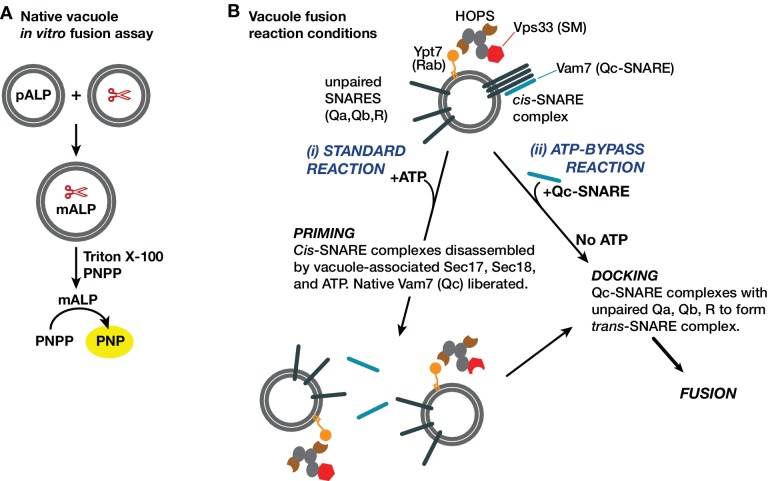
The content-mixing assay and reaction schemes are diagrammed in Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Curves in the dose-response and dose-inhibition experiments are nonlinear fits of the Hill equation. Dashed lines denote data re-plotted from Schwartz and Merz (2009) to facilitate comparison. For all panels, points and bars denote the mean (+or ± s.e.m.) of ≥3 independent experiments. (A) Recombinant Qc-2∆, Qc-3∆, and Qc-4∆ proteins are nonfusogenic in no-ATP ‘bypass’ gain-of-function assays. In these assays no ATP, Sec17, or Sec18 are added to the vacuoles (as shown in Figure 3—figure supplement 1, reaction ii). The approximate concentration of endogenous cytoplasmic Vam7 in vivo is indicated (Thorngren et al., 2004). (B) Qc-3∆ and Qc-4∆ are efficient competitive inhibitors of native Qc-wt. In these ATP-containing reactions, endogenous Sec17 and Sec18 are active and fusion is driven by native Qc-wt (Vam7) liberated from cis-SNARE complexes on isolated vacuoles, as diagrammed in Figure 3—figure supplement 1, reaction i. The approximate concentration of native Vam7 in a standard +ATP vacuole fusion reaction is indicated (~16 nM; Thorngren et al., 2004). (C) Added Sec17 restores fusion activity to Qc-3∆ and −4∆ in no-ATP ‘bypass’ assays. The reactions were set up as in panel A, except that the reactions were supplemented with 300 nM Sec17. (D) Sequence alignment of SNAREs in the layer +4 to+5 region. S.c., Saccharomyces cerevisiae; H.s., Homo sapiens; D.m., Drosophila melanogaster. A conserved arginyl (R) residue is indicated in red. (E) Ability of Qc-5∆ variants to promote fusion in no-ATP ‘bypass’ assays. The reactions were set up as in panel A. (F) Competitive inhibition of fusion by Qc-5∆ variants. The reactions were set up as in panel B. (G) Sec17 rescue in gain of function assays with Qc-2∆, Qc-3∆, and Qc-5∆ variants. The no-ATP ‘bypass’ reactions were set up as in panel A, except that the Qc-∆ proteins were always used at 100 nM, and a subset of the reactions were supplemented with 300 nM Sec17, as indicated.