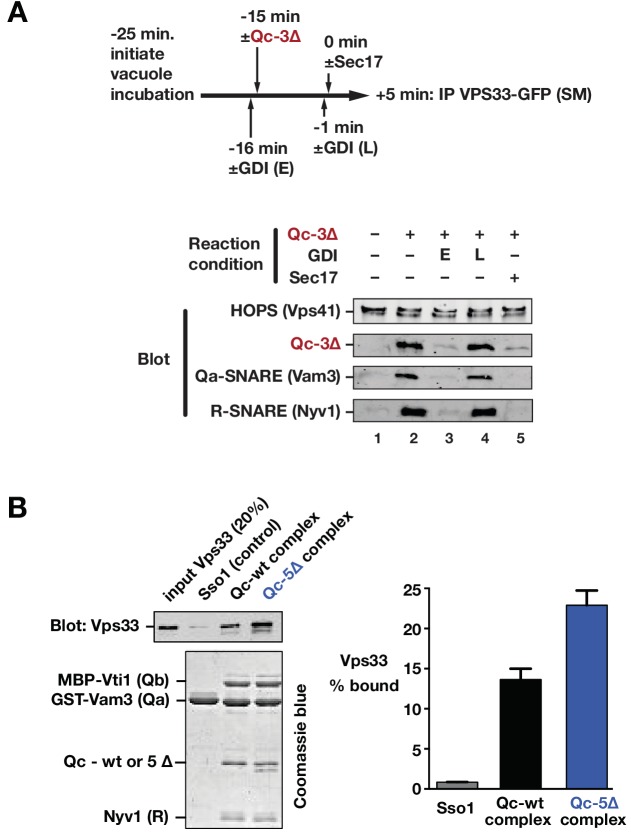
Figure 9. Sec17 and SNARE zippering regulate SNARE interactions with HOPS and Vps33.
(A) Analysis of HOPS-SNARE interactions during a Qc-3∆ block and Sec17 rescue. No-ATP ‘bypass’ reactions were set up similarly to the fusion reactions in Figure 8B, except that only vacuoles isolated from protease-deficient cells expressing Vps33-GFP were used. The vacuoles were pre-incubated for 10 min at 27°C. Qc-3∆ (75 nM) was then added to initiate the assembly of partially zipped trans-complexes. The reactions were incubated for an additional 10 min, and fusion was triggered by adding Sec17 (300 nM). The Rab inhibitor GDI (2.4 µM) was added at early (E) or late (L) time points (lanes 3 and 4). 5 min after Sec17 addition, the vacuoles were sedimented and dissolved in nonionic detergent, and Vps33-GFP was immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibodies. The precipitates were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblot. (B) Interactions of purified Vps33 monomer with vacuolar SNARE complexes. Complexes containing either Qc-wt or Qc-5∆, or the Golgi SNARE Sso1 (control) were assembled on glutathione-agarose resin, and used in pulldowns with soluble, purified recombinant Vps33 as described previously (Lobingier et al., 2014). After washing, the resin-associated material was separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed either by immunoblotting for Vps33-GFP or by Coomassie blue staining. The band intensities for Vps33 were quantified in three independent experiments and are plotted as mean ± s.e.m.