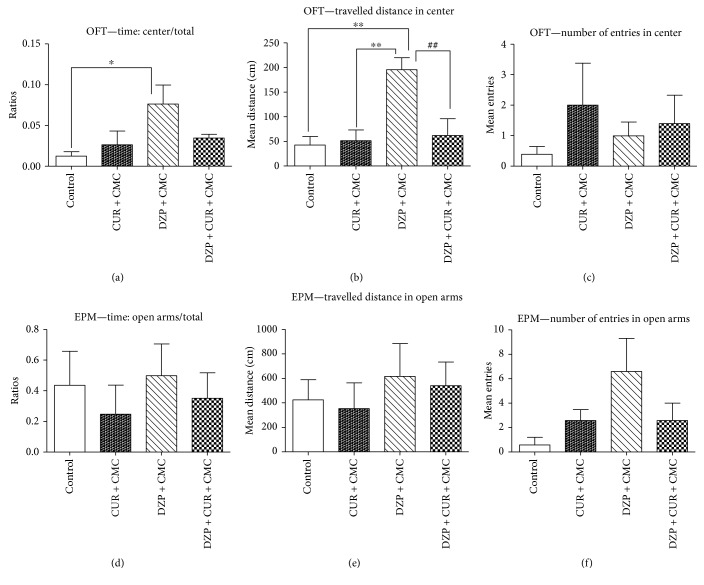
Figure 4.
The effects of curcumin on emotionality in the open field test (OFT) (a, b, c) and in the elevated plus maze (EPM) (d, e, f). The center time/total time ratio (a) increased in the diazepam-treated group as compared to the control group (p < 0.05). The travelled distance in the center (b) enhanced in diazepam-treated rats as compared to the curcumin and control group (p < 0.01). The DZP + CUR + CMC group exhibited lower scores as compared to DZP + CMC (p < 0.01). The number of entries in the center (c) diminished in the diazepam group as compared to other groups, without significant statistical difference. The open arms/total time ratio (d) increased 1.41 times in DZP + CMC as compared to DZP + CUR + CMC. The travelled distance in open arms (e) increased 1.14 times in DZP + CMC as compared to DZP + CUR + CMC. The number of entries in open arms (f) increased 2.53 times in DZP + CMC as compared to DZP + CUR + CMC. The differences for emotionality (d, e, f) in the EPM were not statistically significant. Each group consisted of 5 rats. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05 as compared with control/CUR + CMC; ∗∗p < 0.01 as compared with control/CUR + CMC; and ##p < 0.01 as compared with DZP + CMC.