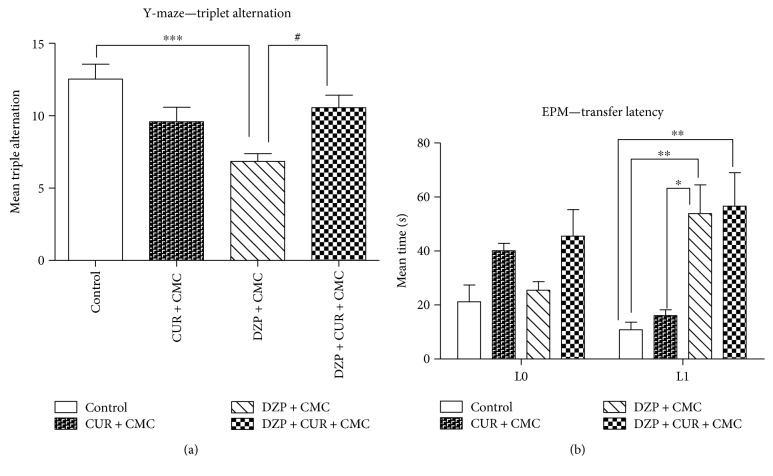
Figure 5.
The effects of curcumin administration on memory in the Y-maze (a) and elevated plus maze (EPM) (b). The DZP group exhibited a significantly higher number of errors (a) in the Y-maze test as compared to the control group (p < 0.001). Conversely, curcumin administration significantly reversed the impairment of spontaneous alternation behavior (p < 0.05). Diazepam administration increased the transfer latency (b) both as compared to curcumin (p < 0.05) and as compared to the control group (p < 0.01) in L1. Each group consisted of 5 rats. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05 as compared with control/CUR + CMC; #p < 0.05 as compared with DZP + CMC; ∗∗p < 0.01 as compared with control/CUR + CMC; and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 as compared with control/CUR + CMC.