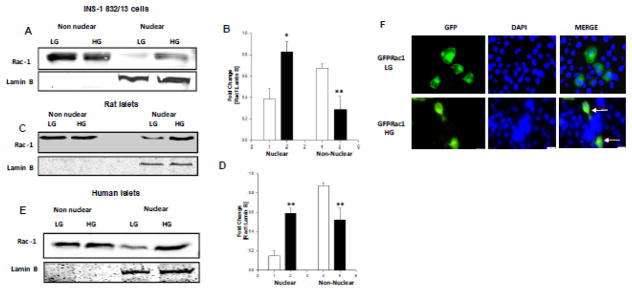
Figure 1. HG conditions promote nuclear accumulation of Rac-1 in INS-1 832/13 cells, normal rat islets and human islets.
Panel A: Relative abundance of Rac1 in the nuclear and non-nuclear fractions isolated from INS-1 832/13 cells exposed to LG or HG conditions was determined by Western blotting.
Panel B: Pooled data from three independent experiments is shown. Accumulation of Rac1 was calculated as a ratio of Rac1 to lamin B in the nuclear fraction [loading control as well as marker] and represented as fold change over basal ** p<0.005 vs 2.5mM glucose.
Panel C: Relative abundance of Rac1 in the non-nuclear and nuclear fractions isolated from normal rat islets exposed to LG or HG conditions was determined by Western blotting.
Panel D: Pooled data from three independent experiments is represented herein. Accumulation of Rac1 was calculated as above. ** p<0.005 vs 2.5mM glucose alone,*p <0.05 vs 20 mM glucose alone.
Panel E: Human pancreatic islets were incubated with LG or HG for 24 hours and relative abundance of Rac1 in the non-nuclear and nuclear fractions was determined by Western blotting. A Western blot of one batch of human islet lysates is provided here.
Panel F: WT GFP Rac1 was transfected 24 hours treated with LG and HG for 24 hours. DAPI was used to counter stain the nucleus. Nuclear association of Rac1 is indicated by arrows.