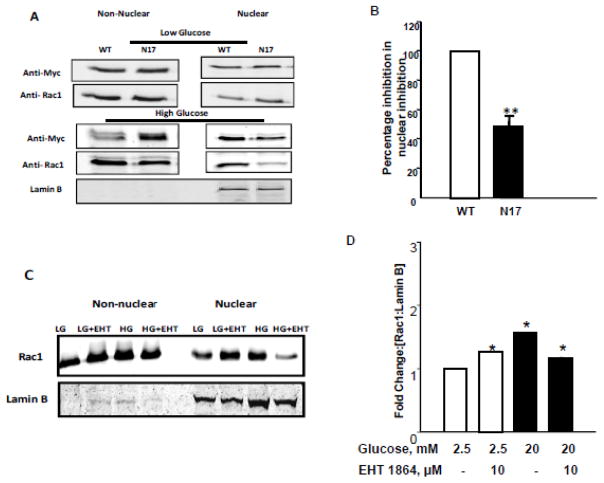
Figure 2. Active configuration of Rac-1 [GTP-bound form] is necessary for nuclear accumulation under HG exposure conditions.
Panel A: INS-1 832/13 cells were transfected with either myc-tagged wild type [WT] or dominant negative Rac1 [N17] prior to exposure to HG conditions. Accumulation of Rac1 was assessed by Western blotting.
Panel B: Pooled data from three independent experiments are shown in the graph ** p<0.005 vs WT Rac1.
Panel C: INS-1 832/13 cells were treated with LG or HG in presence or absence of EHT1864 (10 μM), a specific small molecule inhibitor of Rac1, for 24 hrs. Cells were then pelleted and subjected to nuclear fractionation using NE-PER kit according to manufacturer’s instructions.
Panel D: Inhibition of HG-induced nuclear translocation by EHT 1864, was quantified by densitometric analysis. Results were expressed as mean fold change from three independent experiments *p <0.05 vs 20 mM glucose.