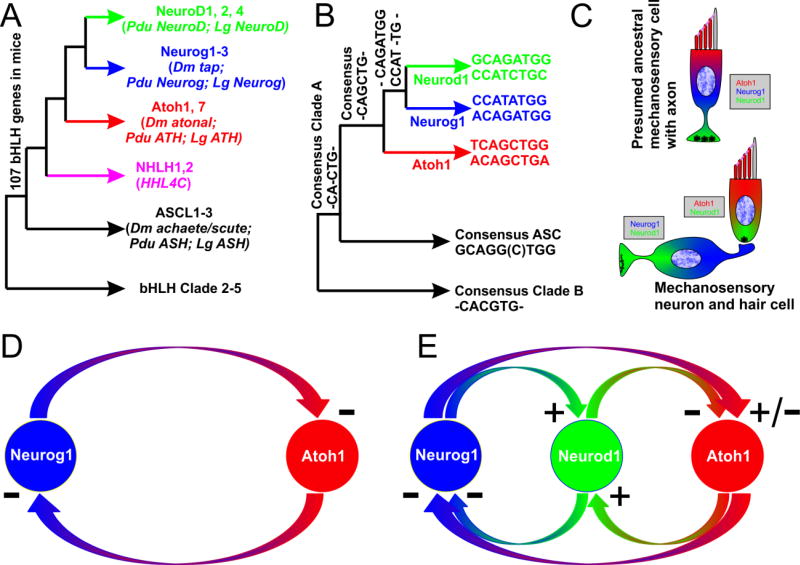
Figure 2. Relationship of the bHLH transcription factors and their E-boxes indicates likely multiplication and diversification at molecular and cellular levels.
(A) Relationship between the bHLH transcription factors. (B) Relationship between the E-box binding sites of the various bHLH transcription factors. Note co-evolutionary changes in the bHLH transcription factors (A) and the E-box sequences (B). (C) The presumed ancestral mechanosensory cell with an axon may have contained three bHLH transcription factors: Atoh1, Neurod1, and Neurog1. Incomplete segregation of these three transcription factors result in a derived condition with separate hair cells expressing Atoh1 and Neurod1 and sensory neurons expressing Neurod1 and Neurog1. Some experiments suggest that Neurog1 and Atoh1 are in a negative feedback loop [D (Raft et al., 2007)]. Knockin of Neurog1 into Atoh1 and effects of Neurod1 deletion suggest that this feedback loop is more complicated and at least in part mediated by Neurod1 (E). Modified after (Fritzsch et al., 2010; Pan et al., 2012b)