Figure 2.
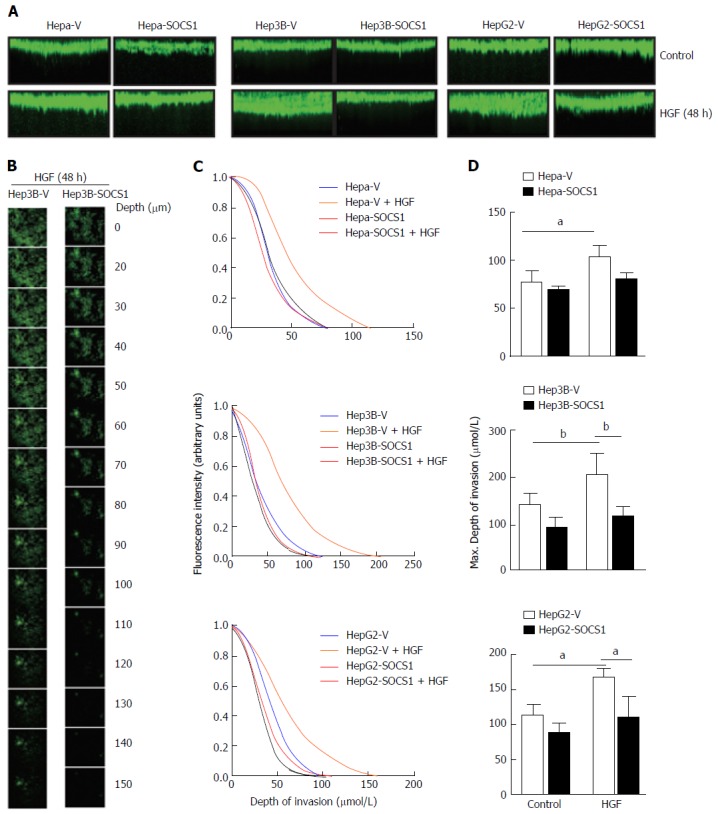
Inhibition of hepatocyte growth factor-induced invasion of collagen matrix by suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepa-V and Hepa-SOCS1, Hep3B-V and Hep3B-SOCS1, and HepG2-V and HepG2-SOCS1 cell lines were evaluated for their ability to invade collagen matrix in a 3-D invasion assay in the presence or absence of mouse HGF (25 ng/mL for Hepa cells) or human HGF (30 ng/mL for Hep3B, HepG2 cells). After 48 h, cells were fluorescently labeled with calcein Green, fixed and examined by confocal microscopy. A: The reconstructed cross-sectional images of cell migration, representative of two independent experiments, are shown; B: Representative images of Hep3B-V and Hep3B-SOCS1 cells migrated to different planes of the collagen-agarose matrix along the z-axis; C: Efficiency of migration (ratio of the fluorescence intensity at each 5 μm layer over the fluorescence intensity of the non-invaded cells at the top 5 μm); D: Maximum depth of invasion by control and SOCS1-expressing cells in the absence or presence of HGF. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. SOCS1: Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1.
