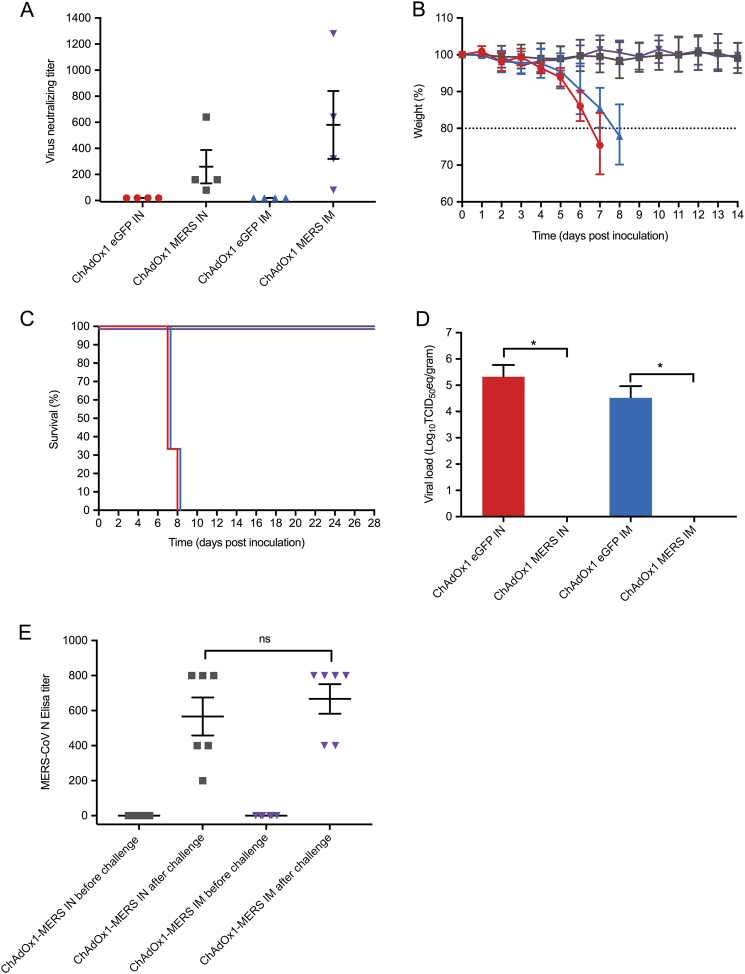
Fig. 1.
Protective Efficacy of ChAdOx1 MERS vaccine. Groups of 10 mice were vaccinated with 108 Infectious Units (IU) ChAdOx1 eGFP or ChAdOx1 MERS via the intranasal or intramuscular route, blood samples were collected before vaccination, and before challenge at 28 days post vaccination. hDPP4 mice were challenged intranasally with 104 TCID50 MERS-CoV (strain HCoV-EMC2012), four animals of each group were euthanized at 3 days post inoculation for serological, virological and histopathological analyses. All analyses were performed in duplicate. a Neutralising antibody titre of hDPP4 mouse serum samples against MERS-CoV strain HCoV-EMC/2012 after vaccination (n = 4 per group). b Weight loss after intranasal challenge with 104 TCID50 MERS-CoV, (n = 6 per group). c Survival curves of the vaccinated groups (n = 6 per group). d Mean ± SD of MERS-CoV viral loads in the lower respiratory tract of vaccinated hDPP4 mice at 3 dpi (n = 4 per group). e Nucleocapsid ELISA responses (n = 6 per group). All experimental procedures were performed as previously described.16 Red = ChAdOx1 eGFP intranasally vaccinated animals; Grey = ChAdOx1 MERS intranasally vaccinated animals; Blue = ChAdOx1 eGFP intramuscularly vaccinated animals; Purple = ChAdOx1 MERS intramuscularly vaccinated animals